The Beginnings
- Taking on the Automotive Business Setting Course to Enter Automotive Business
-
Visiting Europe and the U.S. to study the automotive industry
- 1929
-
Kiichiro Toyoda traveled overseas to gather information on the U.S. machine and automotive industries, and signed a patent transfer agreement with Platt Brothers & Co., Ltd. in the UK.
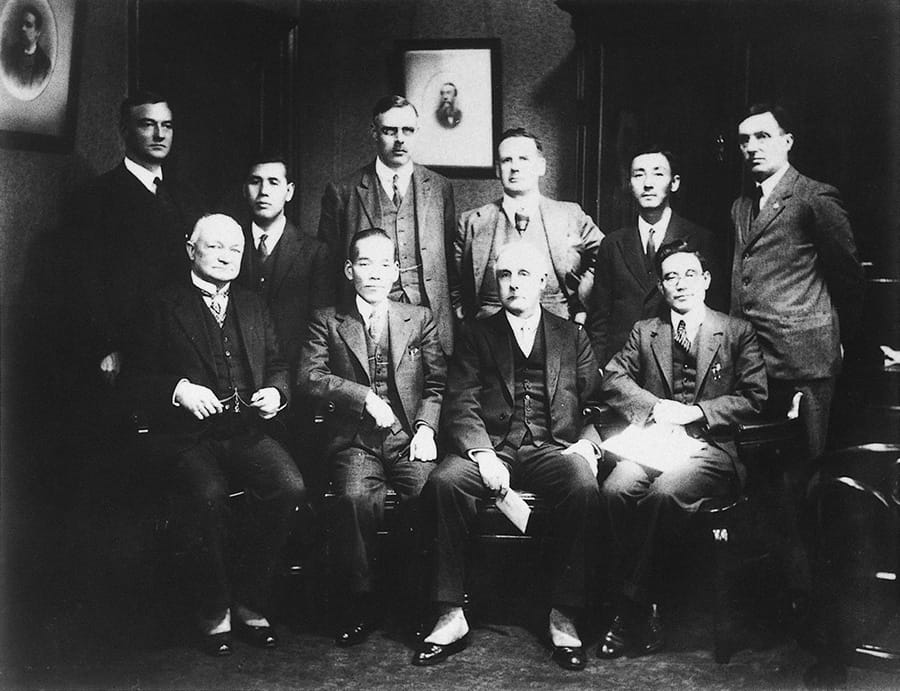

Signing of the patent transfer agreement with Platt Brothers & Co., Ltd.
-
Research and development of domestic automotive manufacturing
- 1930
-
Kiichiro Toyoda commenced automotive surveys and research
- 1935
-
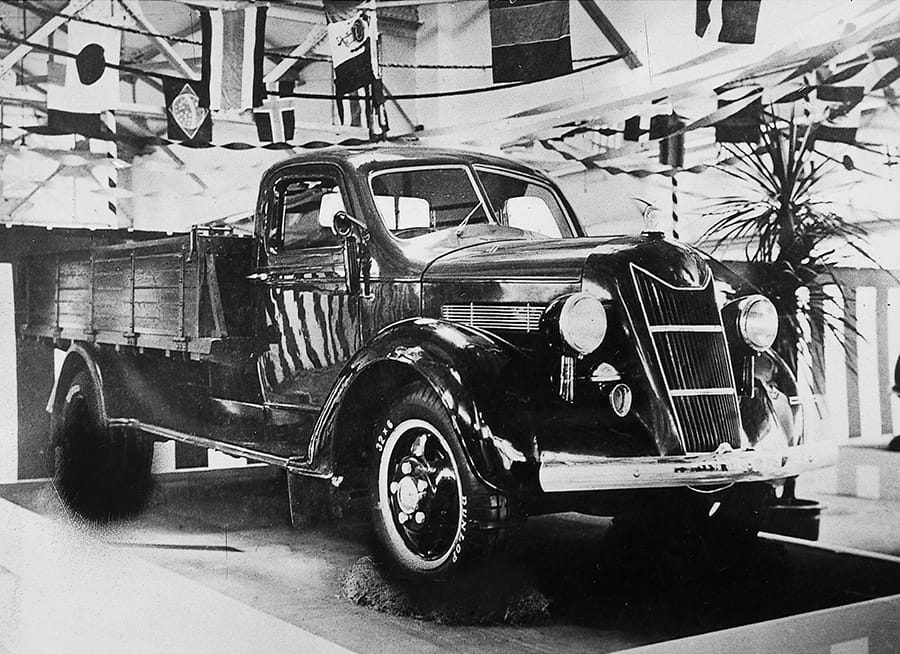
Toyoda Model G1 Truck debuted

- 1936
-
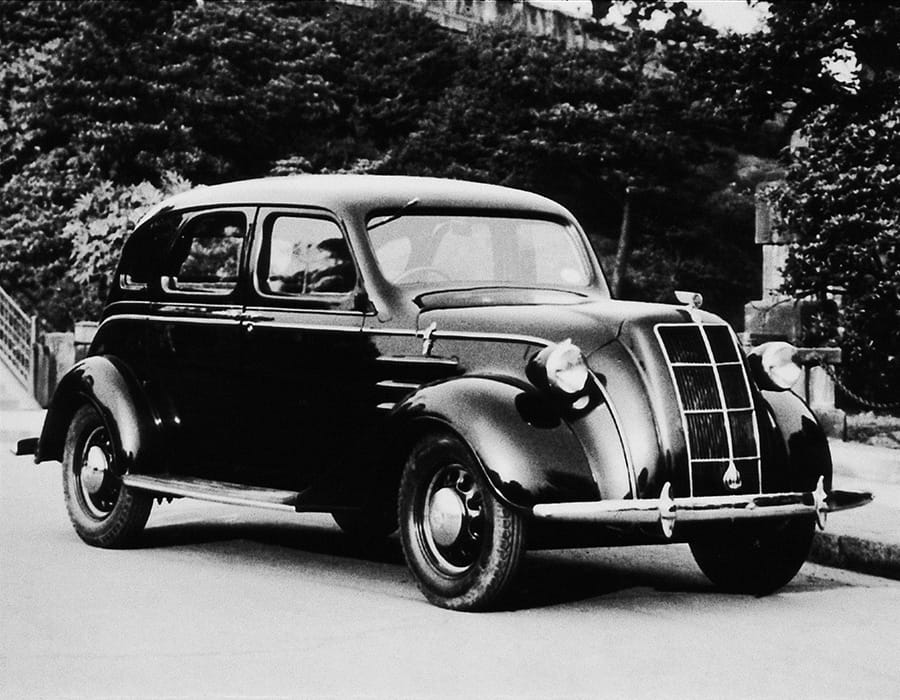
Toyoda Model AA debuted

-
Preparations for entry into the automotive industry
- 1933
-
Toyoda Automatic Loom Works established Automotive Division
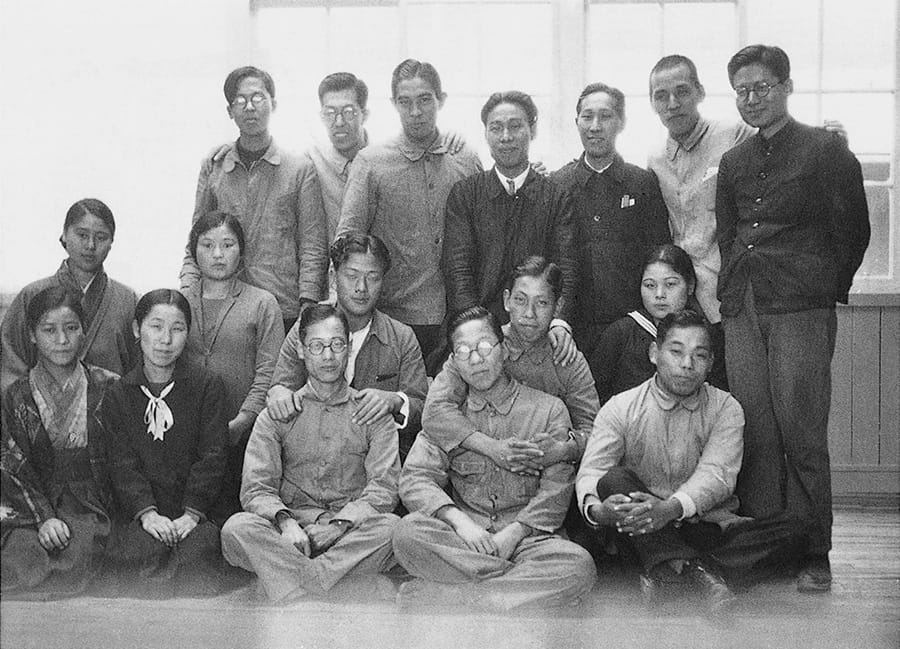

The founding staff of the Automotive Division
- 1935
-
Five Main Principles of Toyoda established

- 1936
-
Toyota logo established

- From 1937 Establishment of Toyota Motor Co., Ltd.
-
New Toyota Motor Co., Ltd.
- 1937
-
Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. Established
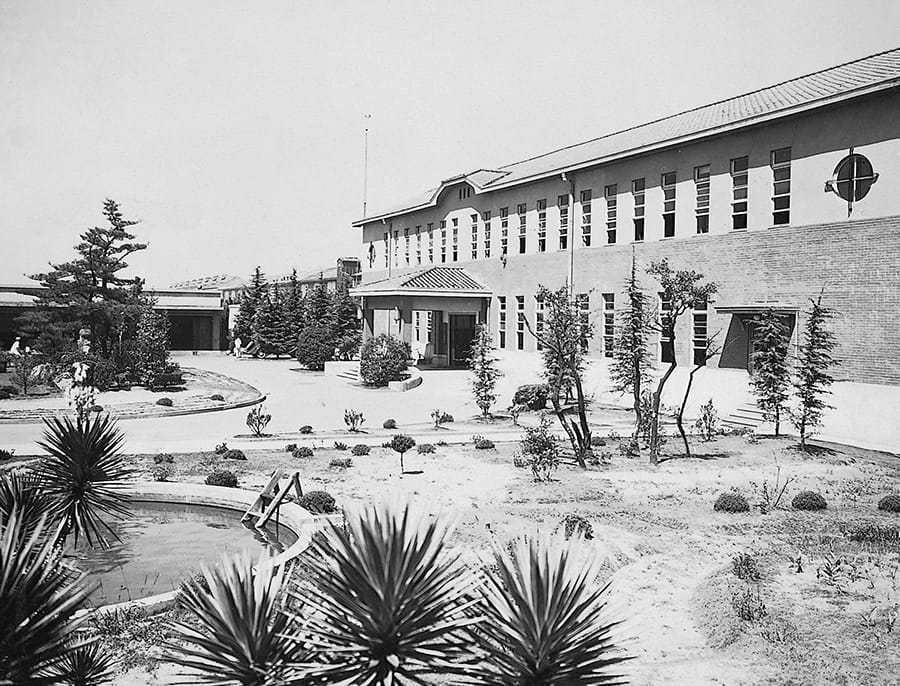

Main office
-
- 1937
-
Risaburo Toyoda appointed president, and Kiichiro Toyoda appointed vice president
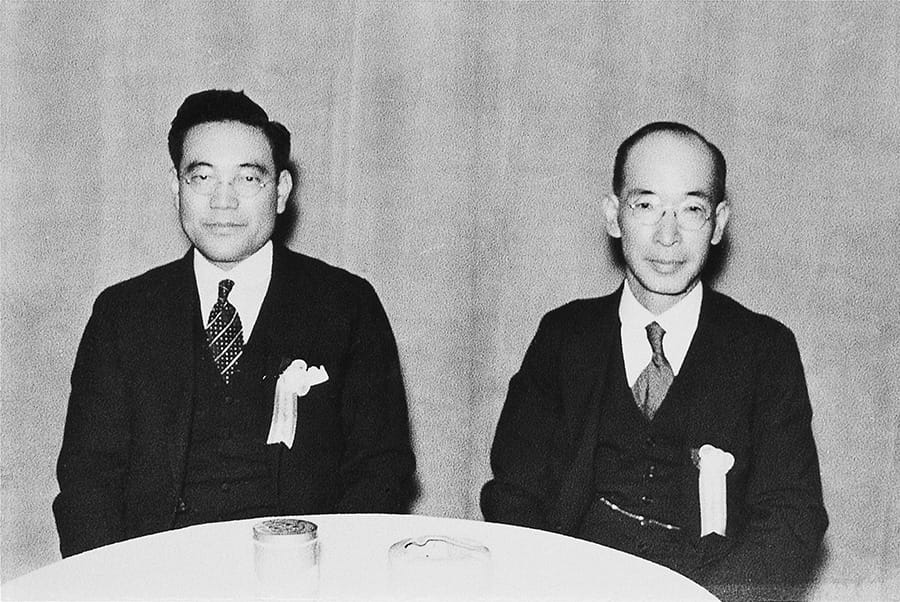

Left: Vice President Toyoda, Right: President Toyoda
-
Operation of Toyota's first plant commences
- 1938
-
Koromo Plant (now Honsha Plant) operations started
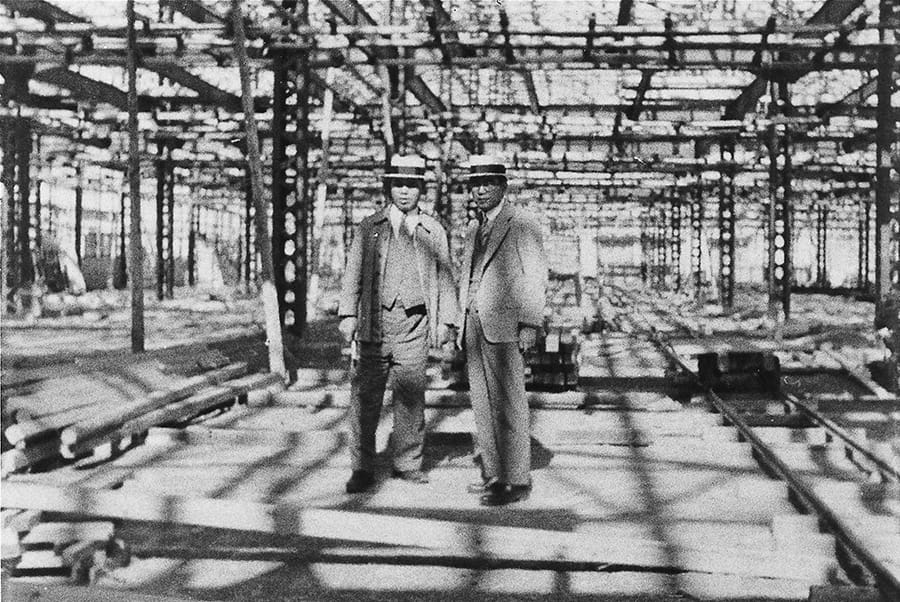

Kiichiro Toyoda inspecting the plant under construction
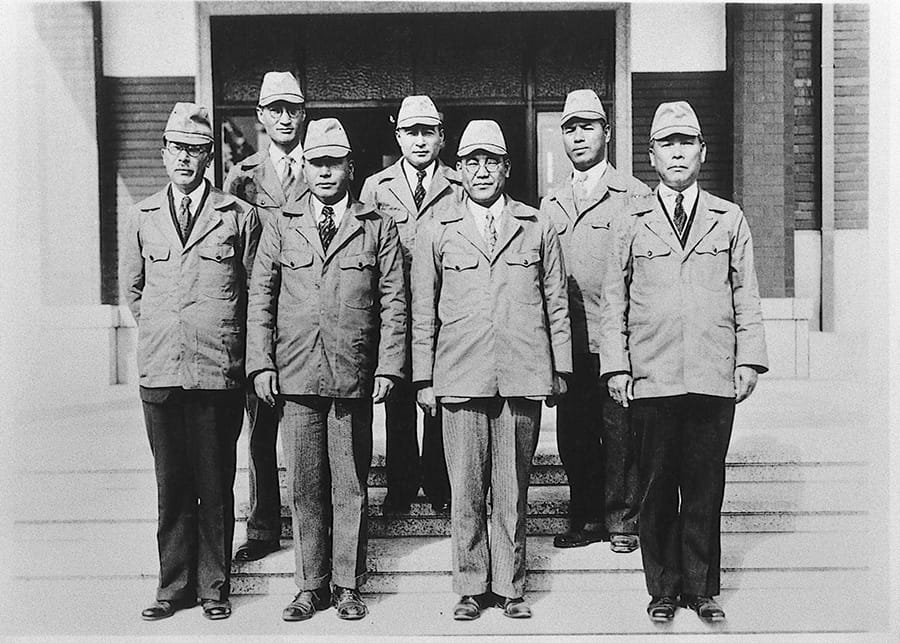

Toyota executives on the day of Koromo Plant's foundation
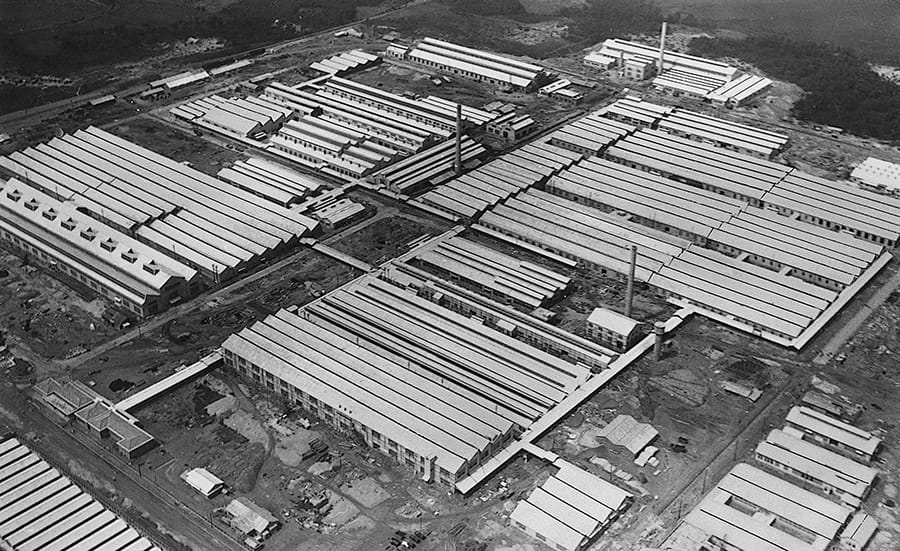

Koromo Plant (now Honsha Plant)
- 1938
-
Just-in-Time system launched
-
- 1938
-
Toyoda Model GB Truck launched

-
Control of the automobile manufacturing industry under a wartime economy
- 1938
-
The National Mobilization Law put into force by the Japanese government, which regulated the distribution of materials and fuel for automotive manufacturing
-
- 1939
-
Annual production in Japan reaches 10,000 units
- 1940s Automobile Prototypes, Research and Development of Basic Technology
-
Wartime Production
- 1941
-
Toyota Model AE (Shin Nippon Go) launched Developed to conserve fuel by the request of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry
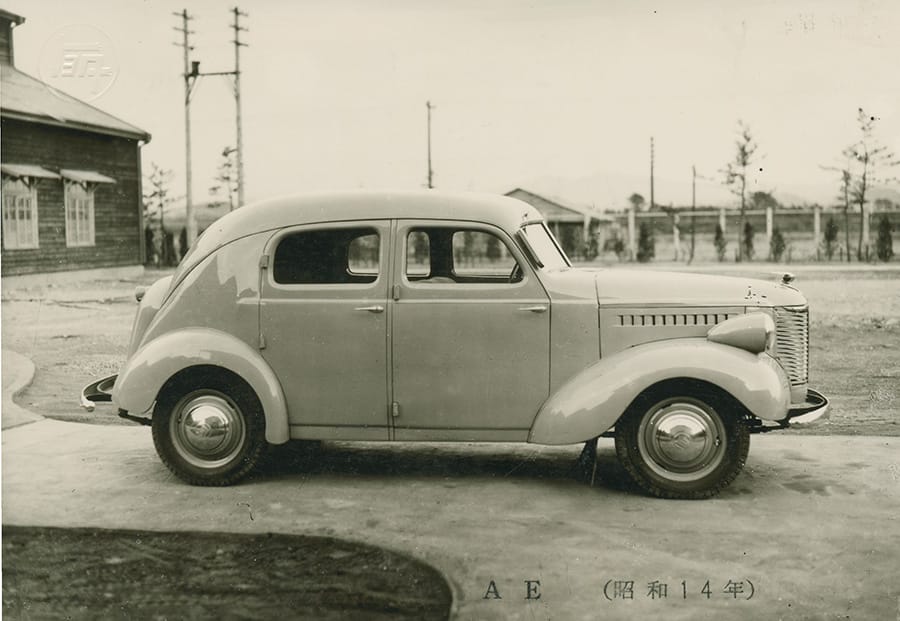

- 1943
-
Toyota Model KC Truck launched Designed to reduce use of steel as specified by the Ministry of Commerce and industry
-
- 1941
-
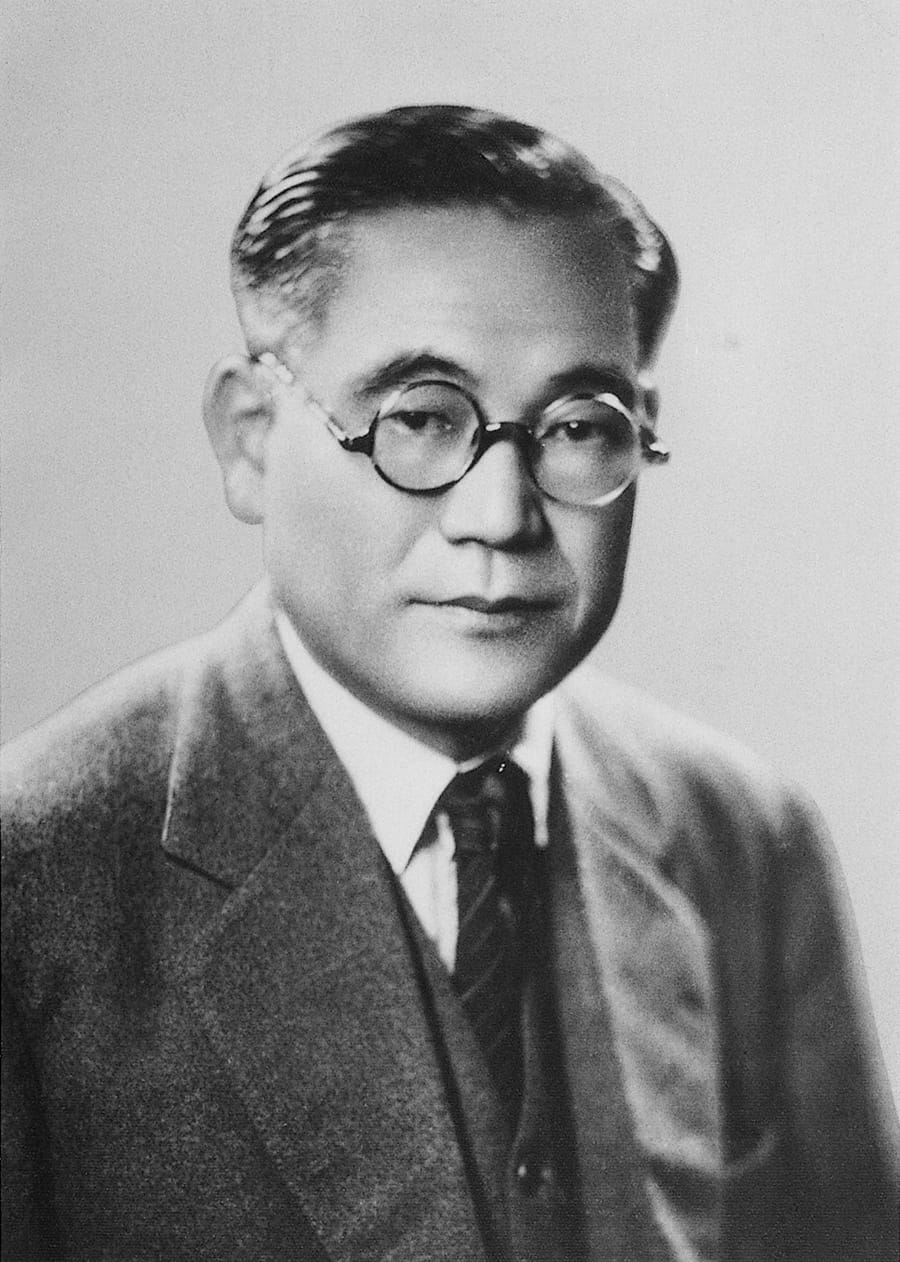
Kiichiro Toyoda appointed president

-
Company reconstruction
- 1945
-
GHQ permitted production of trucks in September Conversion to consumer goods production permitted in December
- 1946
-
Restoring of plant and equipment and the Temporary Reconstruction Office established With Kiichiro himself leading the restoration efforts as the head of the office
- 1946
-
President Kiichiro Toyoda invited national regional distribution representatives to rebuild a dealer network and gave his speech entitled "The Current State of the Automobile Business and the Path Ahead for Toyota Motor Co., Ltd."

-
Development of Compact Car Equipped with the S Engine
- 1947
-
Toyopet Truck Model SB (small truck) launched
- 1947
-
Toyopet Model SA (compact passenger car) launched

- 1948
-
Open test drive of the Toyopet Model SA carried out
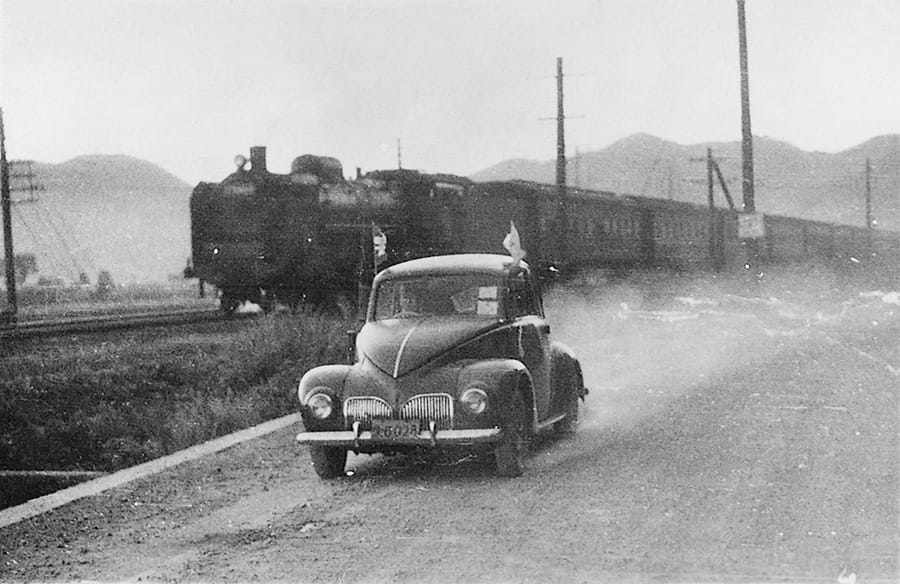

Toyopet Model SA in an open test drive
(Racing against an express train from Nagoya to Osaka)
- 1949
-
Toyopet Model SD (compact passenger car) launched

-
Affiliated companies and future Toyota group member firms established in the 1940s and later
- 1940
-
Toyoda Seiko, Ltd. (now Aichi Steel Corporation)
- 1940
-
Toyoda Physical and Chemical Research Institute
- 1941
-
Toyota Machine Works Co., Ltd. (now JTEKT Co.)
- 1943
-
Tokai Hikoki Co., Ltd. (now Aisin Corporation)
- 1945
-
Toyota Shatai Kogyo Co., Ltd. (now Toyota Auto Body Co., Ltd.)
- 1946
-
Kanto Electric Motor Works, Ltd. (now Toyota Motor East Japan, Inc.)
- 1948
-
Nisshin Tsusho Kaisha, Ltd. (now Toyota Tsusho Corporation)
- 1949
-
Nagoya Rubber Co., Ltd. (now Toyota Gosei Co., Ltd.)
- 1949
-
Nippondenso Co., Ltd. (now Denso Corporation)
- 1950
-
Minsei Spining Co., Ltd. (now Toyota Boushoku Corporation)
- 1953
-
Towa Real Estate Co., Ltd. (now Toyota Fudosan Co., Ltd.)
-
- 1947
-
Cumulative production in Japan reaches 100,000 units
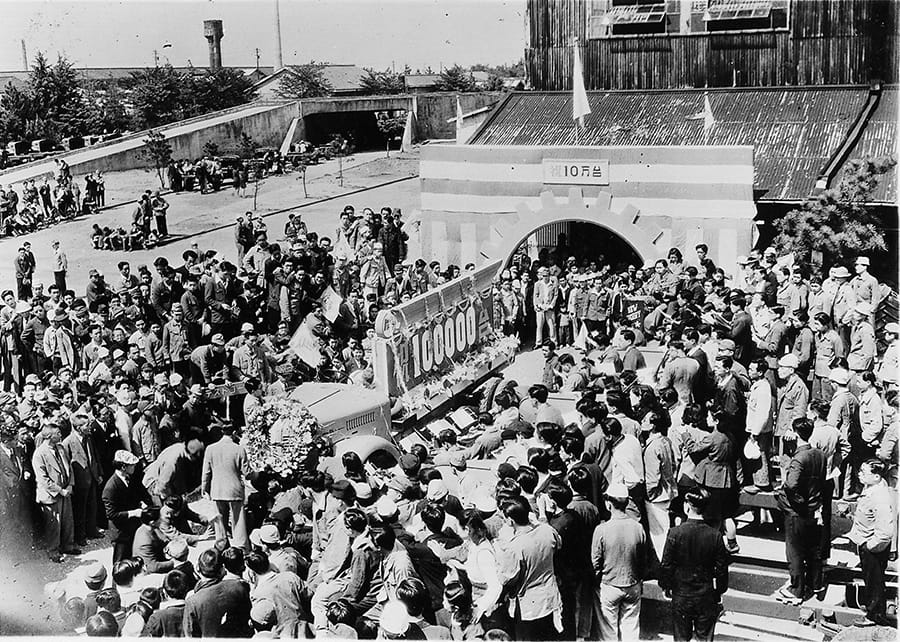

- 1950s Business Management Crisis (Labor dispute); Establishment of Toyota Motor Sales Co., Ltd.
-
Business management crisis
- 1949
-
Dodge Line, a financial and monetary contraction policy, was announced by GHQ and provoked a serious recession
- 1950
-
Deterioration in profitability due to the rising cost of raw materials and the gap between the official price of the product and the market price
- 1950
-
Toyota Motor Sales Co., Ltd. established on April 3 (Shotaro Kamiya appointed president)
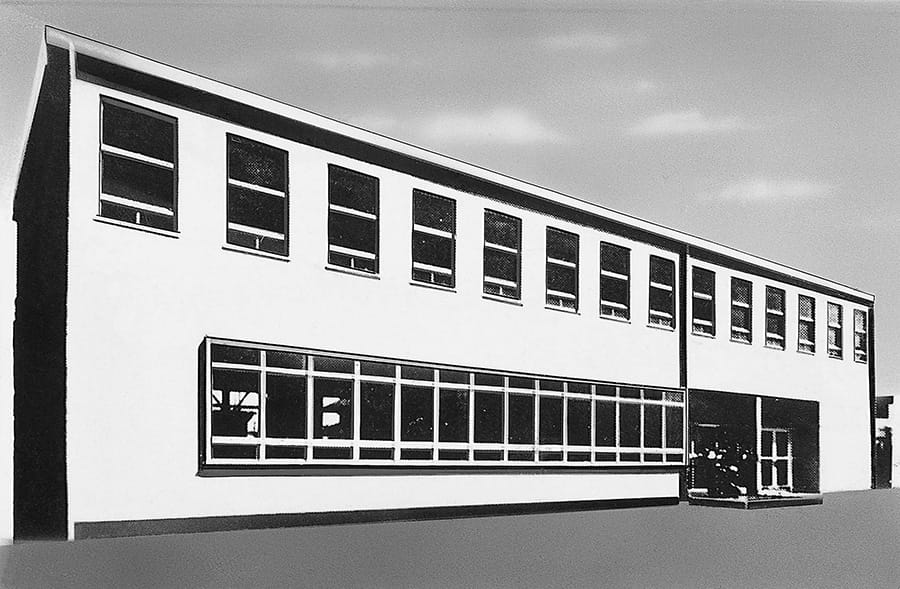
Toyota Motor Sales Co., Ltd.
- 1950
-
A labor dispute over layoffs erupted on April 9
- 1950
-
President Kiichiro resigned to take responsibility for the labor dispute on June 5
- 1950
-
The labor dispute concluded on June 10
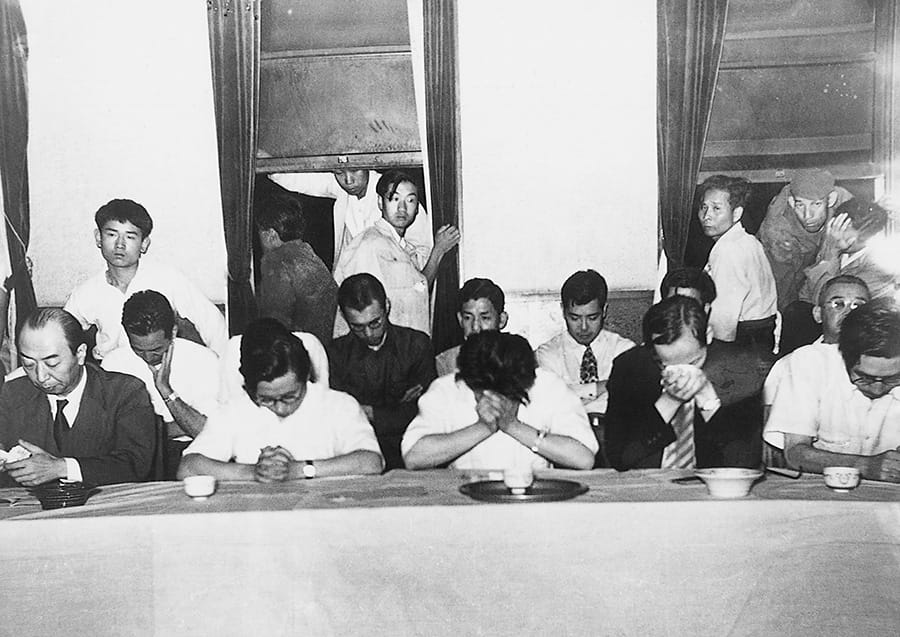

Labor dispute concluded
- 1962
-
Joint Declaration of Labor and Management signed
-
Mass production of four-wheel drive vehicles
- 1951
-
Land Cruiser (BJ) launched

-
Internal systems and programs established
- 1951
-
Facility Modernization Five-Year Plan created
- 1951
-
Creative Idea Suggestion System begun
- 1952
-
Company song and company flag established
- 1953
-
"Good Thinking, Good Products" selected as the corporate slogan

"Good Thinking, Good Products" selected as the corporate slogan
- 1954
-
Main Technical Building (Technical Center) completed
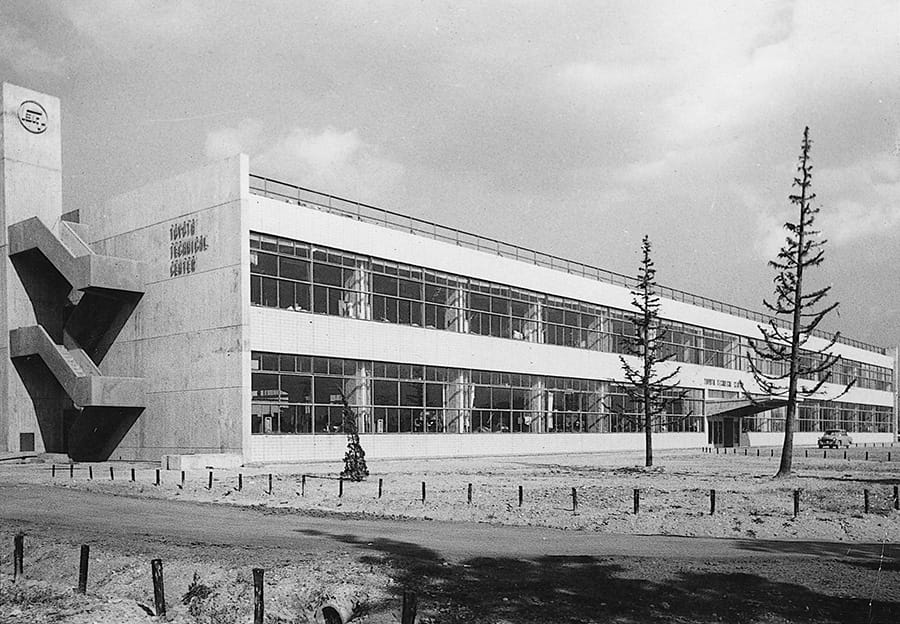

Main Technical Building (Technical Center)
- 1956
-
Honsha Test Track completed
-
Development of a full-fledged passenger car based on Japanese technology
- 1952
-
The R Engine, featuring a major boost in output, completed
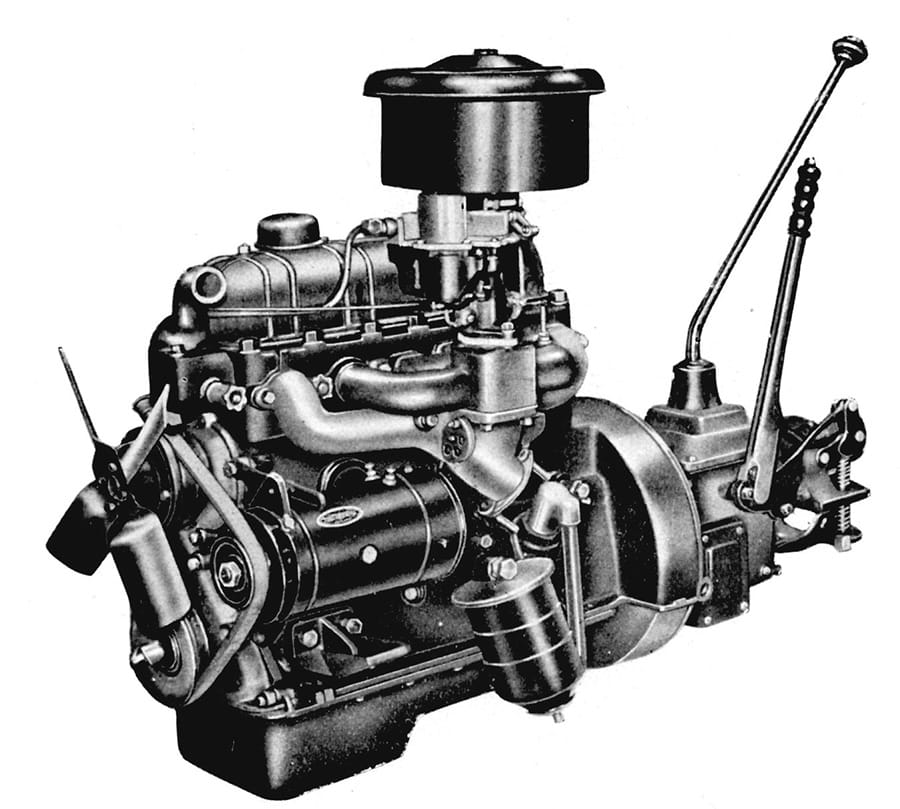
- 1953
-
Toyopet Super Model RH fitted with R engine launched
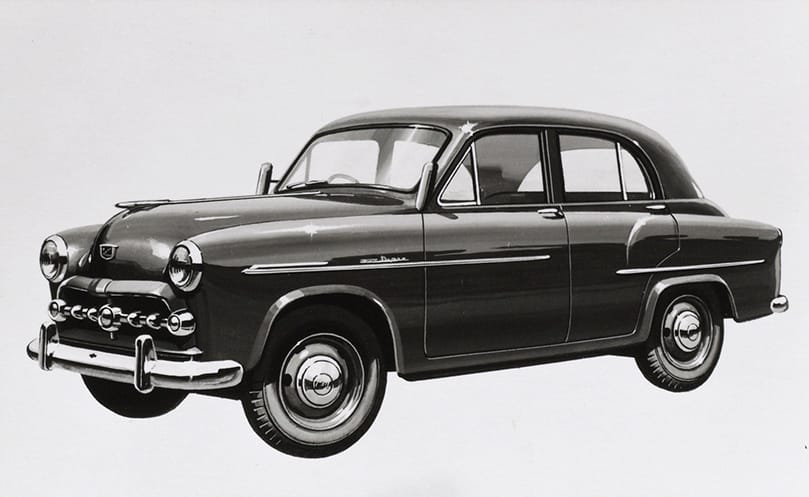

Toyopet Super Model RHK
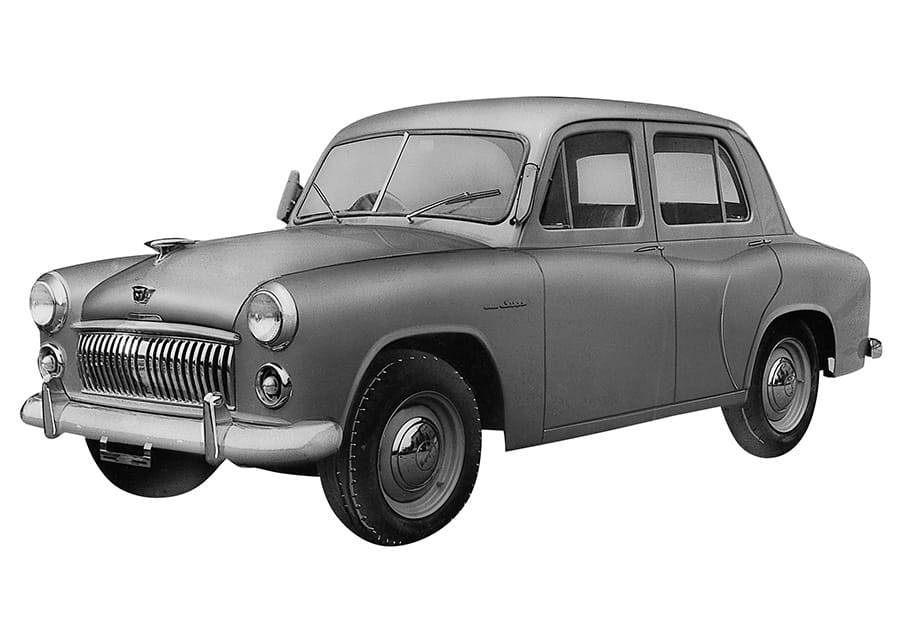

Toyopet Super Model RHN
- 1955
-
Toyopet Crown (Model RS) launched Entirely based on original Japanese technology, from design through manufacturing

-
Toyota's entry into overseas markets
- 1957
-
Crown became first Japanese passenger car to be exported to the U.S
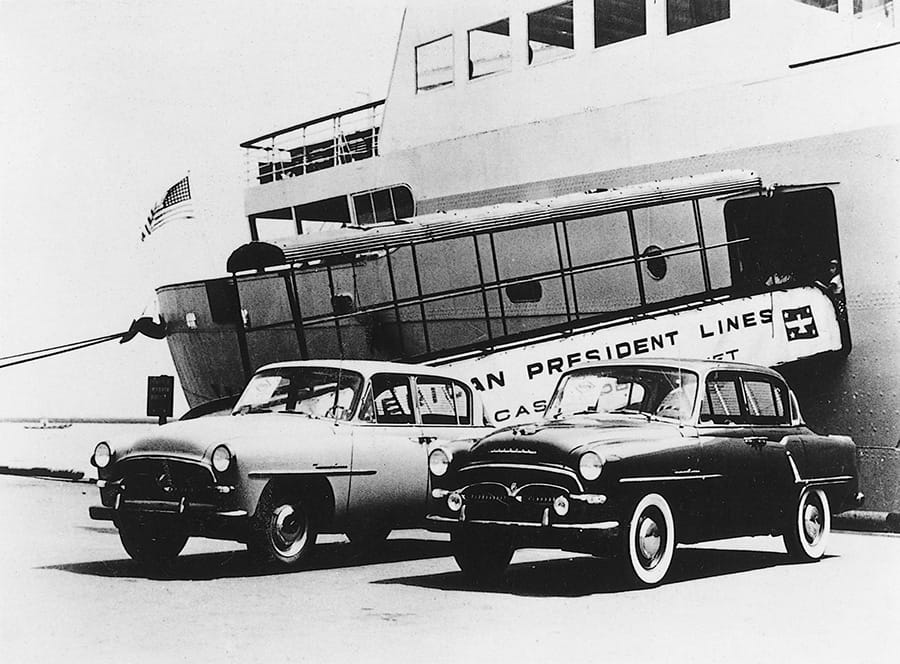

Toyopet Crown shipped to the U.S., marking Japan's first car export to the U.S.
- 1957
-
Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. established
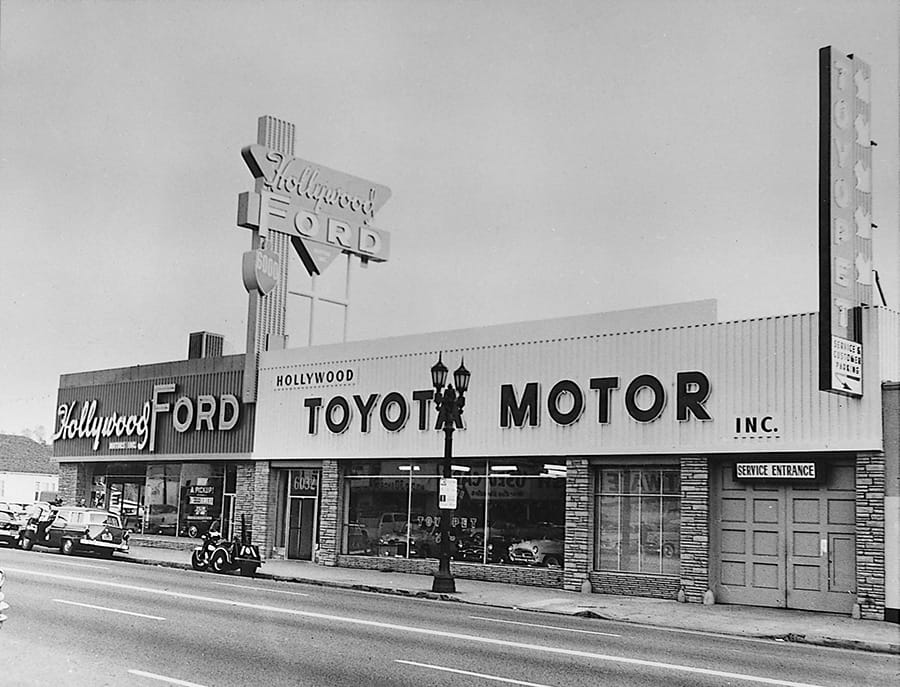

Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc.
- 1958
-
Toyota do Brasil Ltda. (TDB) established
-
Expansion of the automobile market (to accommodate the small car market)
- 1957
-
Toyopet Corona launched

-
- 1959
-
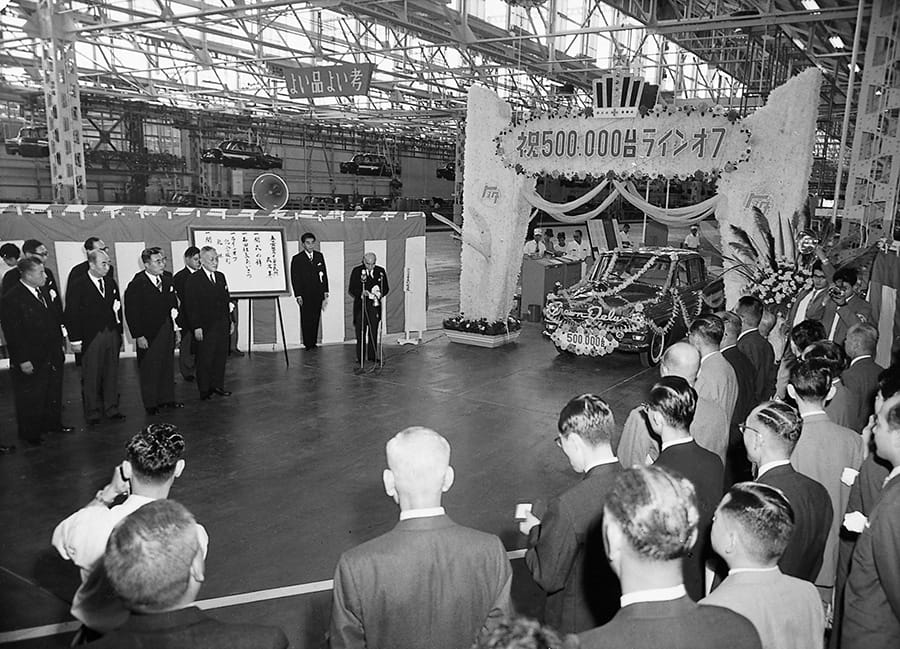
Cumulative production in Japan reached 500,000 units
