Apr. 25, 2018
Plan to Develop Aichi Low-carbon Hydrogen Supply Chain Moves Forward
Chita City
Toyota City
Chubu Electric Power Co., Inc.
Toho Gas Co., Ltd.
Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota Industries Corporation
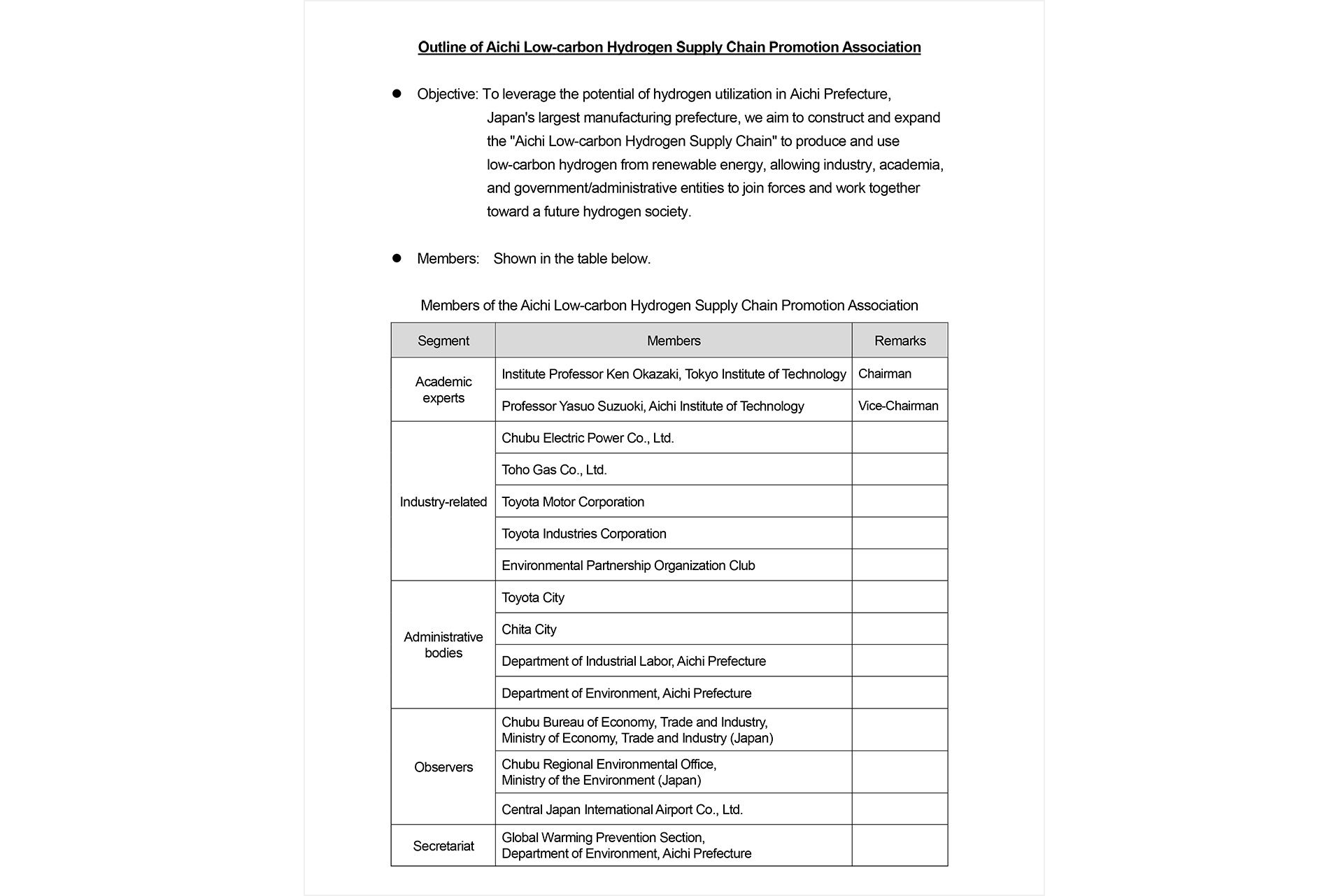
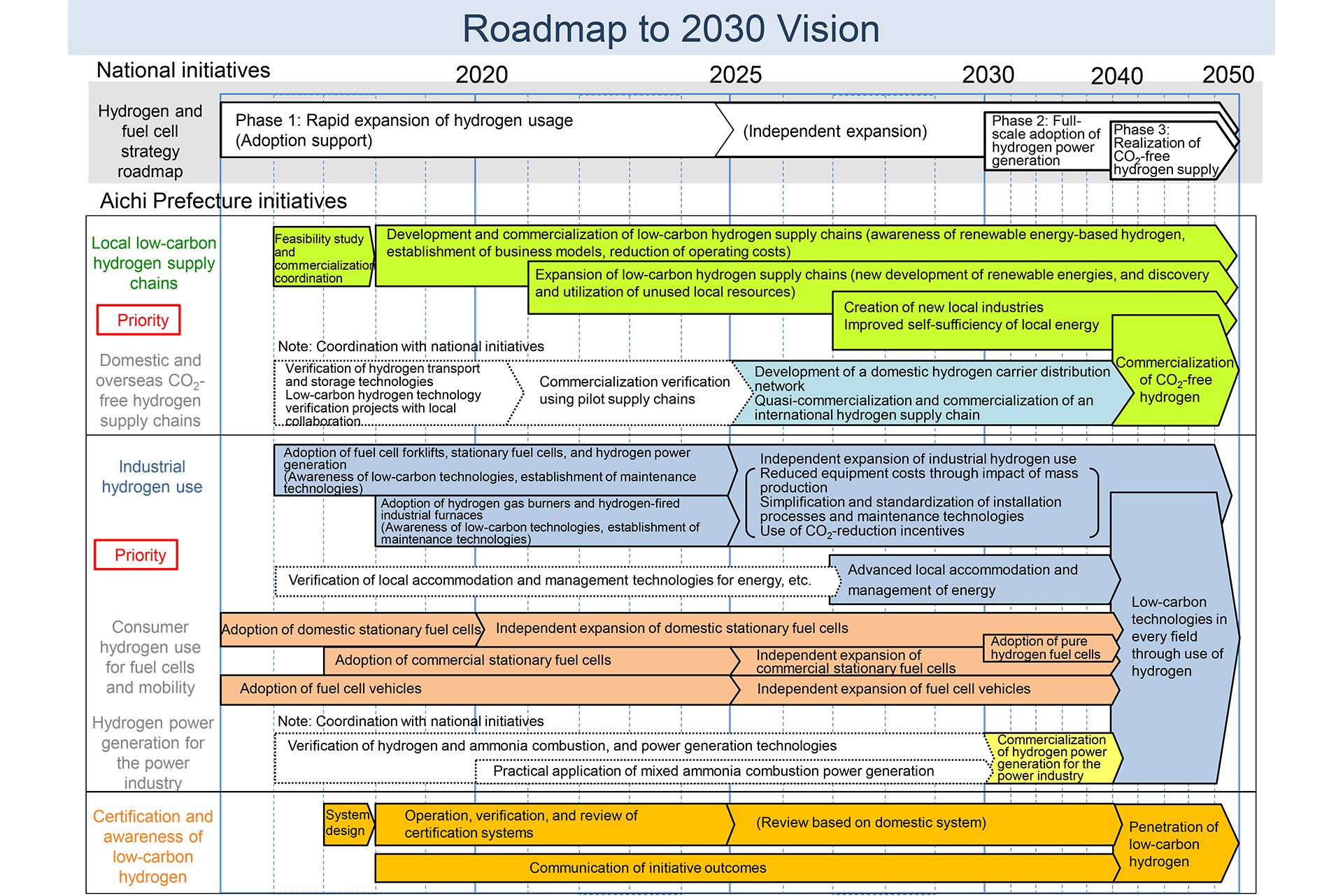
Toyota City, Japan, April 25, 2018―The Aichi Low-carbon Hydrogen Supply Chain Promotion Association*, a body which includes the Aichi prefectural government, companies operating within the prefecture, municipal authorities, and experts, has developed the Aichi Low-carbon Hydrogen Supply Chain 2030 Vision ("2030 Vision"), in addition to a corresponding roadmap. The goal of all entities is the realization of a hydrogen-based society spanning the entire region through mutual coordination and all-inclusive efforts.
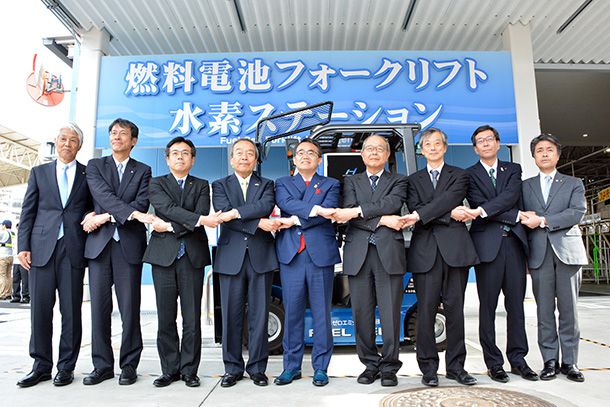
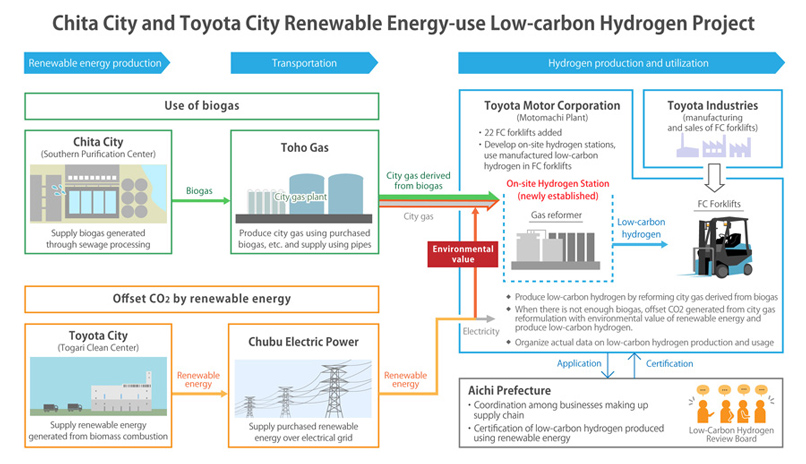
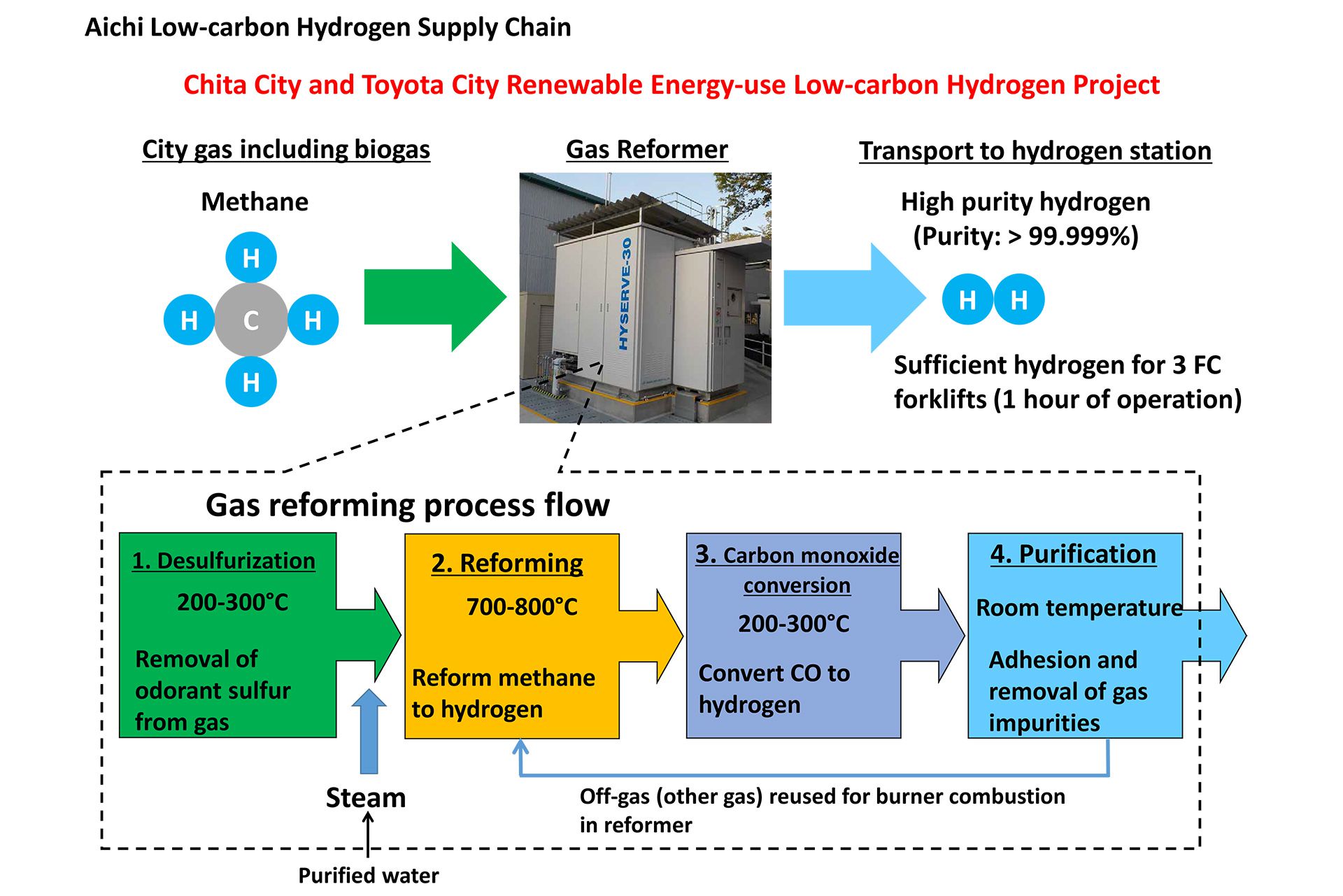
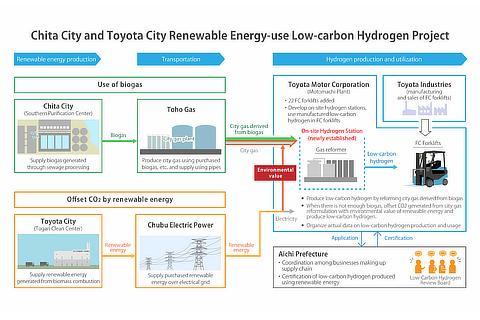
Today, as a first step toward realizing the 2030 Vision, Aichi Prefecture, Chita City, Toyota City, Chubu Electric Power Co., Ltd. (Chubu Electric Power), Toho Gas Co., Ltd. (Toho Gas), Toyota Motor Corporation (Toyota), and Toyota Industries Corporation (Toyota Industries) have launched the Chita City and Toyota City Renewable Energy-use Low-carbon Hydrogen Project ("Project").
*Aichi Low-carbon Hydrogen Supply Chain Promotion Association
The Association was established in October 2017 to promote the commercialization of a low-carbon hydrogen supply chain and to bridge entities including industry, academia, and government throughout the prefecture in order to achieve this. (Chairman: Professor Ken Okazaki, Tokyo Institute of Technology; Vice Chairman: Professor Yasuo Suzuoki, Aichi Institute of Technology.)
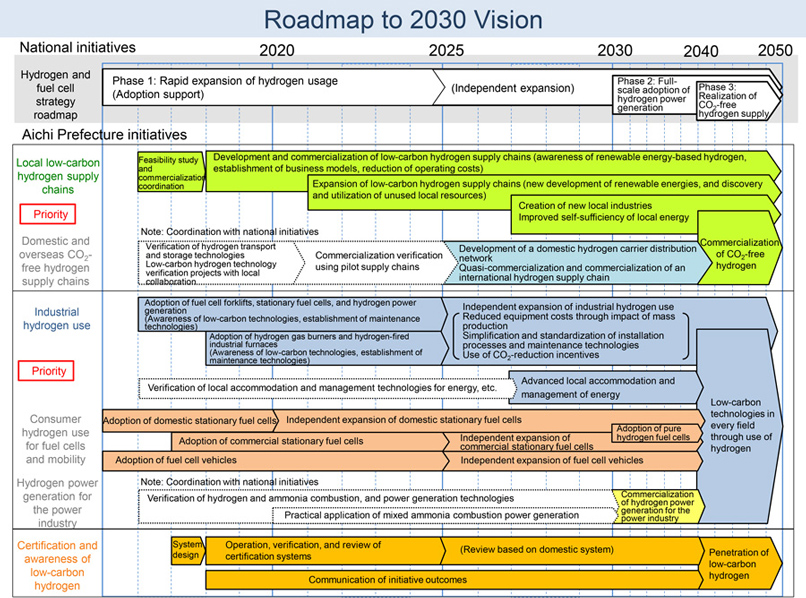
- Outline of the 2030 Vision and the roadmap
- Background
Hydrogen is a useful energy source for realizing a low-carbon society. Without emitting any carbon dioxide (CO2) during use, hydrogen can be produced from renewable resources (including wind power, solar power, and biomass [sewage sludge]) and can be stored and transported for use in various fields. Hydrogen has the potential to support the transition to a low-carbon society, not only in the transportation field, but also in various fields including industrial fields.
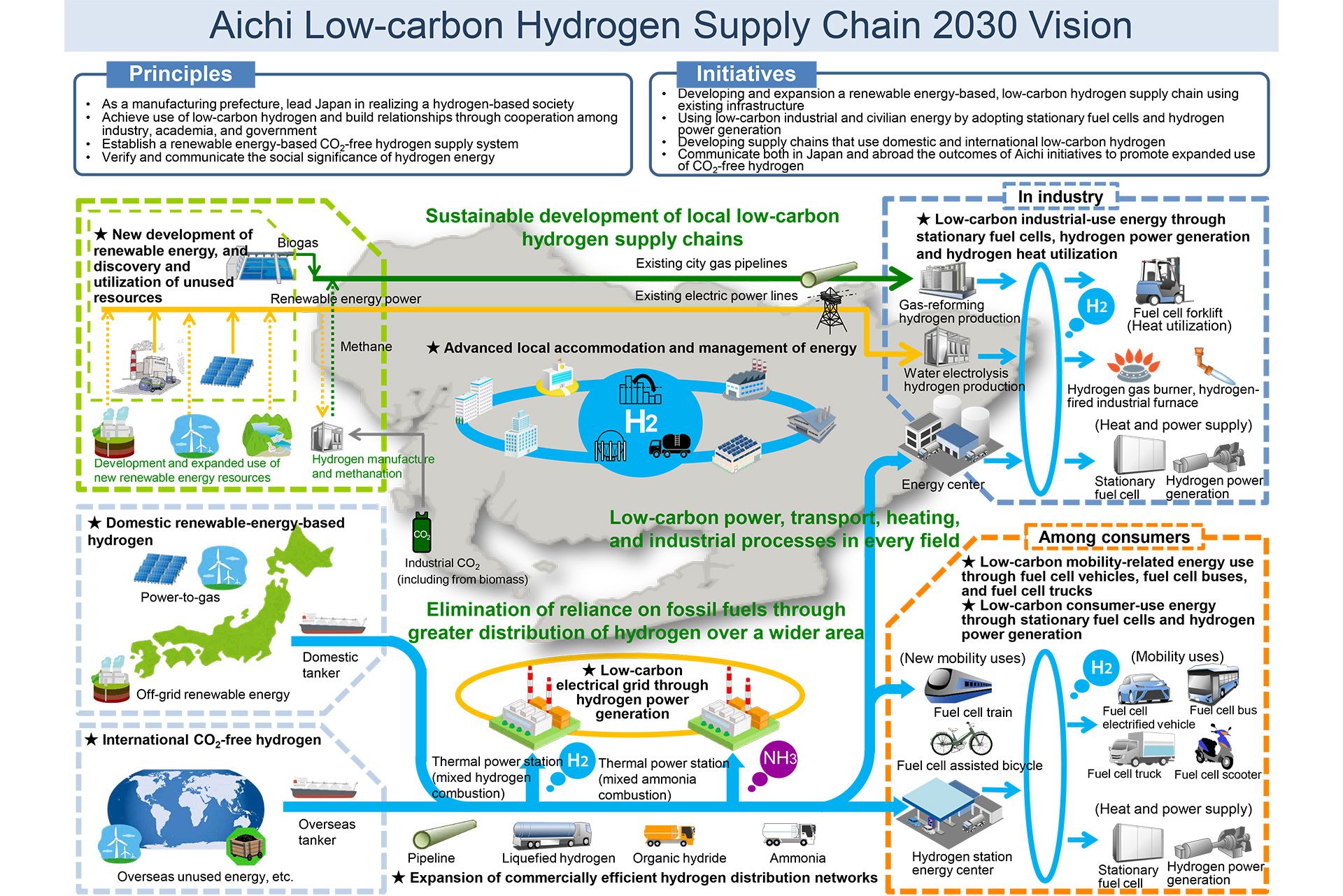
To further promote measures to combat global warming, the low-carbon footprint of the hydrogen supply chain as a whole, through use of renewable resources and the concept of "production, transportation, and use (of hydrogen)," has been promoted in Aichi Prefecture. To meet this goal, shared ownership of the vision is required throughout the region and different entities including industry, academia, and government are expected to work together towards it. In line with this, the Aichi Low-Carbon Hydrogen Supply Chain Promotion Association authored the 2030 Vision, which envisions an Aichi Prefecture in 2030 that makes active use of low-carbon hydrogen in 2030, as well as a roadmap to achieve this.
- Main Points
- Building on the national Strategic Roadmap for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells as well as the Basic Hydrogen Strategy, the 2030 Vision aims to achieve a hydrogen-based society ahead of the rest of country, leveraging the prefecture's experience and expertise in monozukuri (all-encompassing approach to manufacturing).
- The three pillars of the 2030 Vision are "sustained development of a regional low-carbon hydrogen supply chain," "carbon reduction in the various fields of electricity, transport, heating and industrial processes," and "elimination of dependence on fossil fuels through the expansion of hydrogen distribution volumes over a wider area," and we will work on the effective use of low-carbon hydrogen and creating partners in close conjunction with industry, academia, and government.
- By introducing a system in which Aichi Prefecture certifies low-carbon hydrogen objectively and fairly, we will aim to promote the popularization of low-carbon hydrogen according to the roadmap.
- Outline of the Project
- Outline
The Project is designed to construct a subsistent low-carbon hydrogen supply chain to produce, supply, and use hydrogen generated from renewable resources within the prefecture, as the first step toward achieving the 2030 Vision. In this project, Toho Gas is expected to produce city gas using biogas generated from sewage sludge at the Chita City Southern Sewage Treatment Center, which is then transported to Toyota's Motomachi Plant through existing city gas pipelines. The city gas derived from biogas is passed through gas reformers at the Motomachi Plant, whereby low-carbon hydrogen, which is used to power the Toyota Industries fuel cell forklifts (FC forklifts) in the plant, is produced, compressed, and stored. Additionally, by supplying Toyota with renewable energy from Chubu Electric Power generated at the Toyota City Togari Clean Center through heat from waste incineration (biomass incineration heat), CO2 emissions from city gas that would be used when there is a biogas shortage can be offset.
We believe that such efforts are meaningful, not only for this project, but also for expanding the amount of renewable energy that will compose the upstream process of the supply chain. In order to increase awareness of this supply chain, Aichi Prefecture has established a Low-Carbon Hydrogen Certification system that certifies hydrogen produced using renewable energy as "low-carbon hydrogen." The Project received certification today becoming the first project to be certified.
- Division of roles by entity
-
- Aichi Prefecture
- Coordination among project members; certification of low-carbon hydrogen production plan; certification of produced hydrogen
-
- Chita City
- Supply and sale of biogas generated from waste treatment at the Chita City Southern Sewage Treatment Center to Toho Gas
-
- Toyota City
- Supply and sale of renewable energy generated from biomass incineration heat at the Toyota City Togari Clean Center to Chubu Electric Power
-
- Chubu Electric Power
- Purchase of renewable energy from Toyota City; supply and sale of renewable energy to Toyota
-
- Toho Gas
- Purchase of biogas from Chita City; supply and sale of city gas derived from biogas through existing pipelines to Toyota
-
- Toyota
- Reform city gas derived from biogas purchased from Toho Gas; produce, compress, and store low-carbon hydrogen; utilize low-carbon hydrogen for fueling FC forklifts at the hydrogen station in the Motomachi Plant; purchase renewable energy from Chubu Electric Power, which would offset CO2 emissions from city gas used when there is a biogas shortage
-
- Toyota Industries Corporation
- Manufacture FC forklifts and sell them to Toyota
-
- Next steps
The Project is designed to transport renewable energy, such as biogas used for hydrogen production, through the existing energy infrastructure of city gas pipes and the electrical grid to produce and supply hydrogen near where it is used. This will allow costs to be reduced by eliminating the amount of capital investment necessary for the facilities required to compress and transport hydrogen, as well as their maintenance expenses, and to achieve early commercialization through the use of existing energy infrastructure.
In the future, in addition to discovering and using biogas and developing new renewable resources, such as biomass power generation and wind power generation, we intends to expand the deployment of FC forklifts and the use of hydrogen through the early introduction of industrial-use fuel cells and small-scale hydrogen generation inside plants. In anticipation of increased demand for hydrogen in the future, we will create a new sustainable business model based on the Project and promote the 2030 Vision to work on achieving a low-carbon society in Aichi Prefecture.