Jun. 12, 2007
Toyota Develops Next-generation Engine Valve Mechanism
― 'Valvematic' Achieves High Fuel Efficiency and Dynamic Performance ―
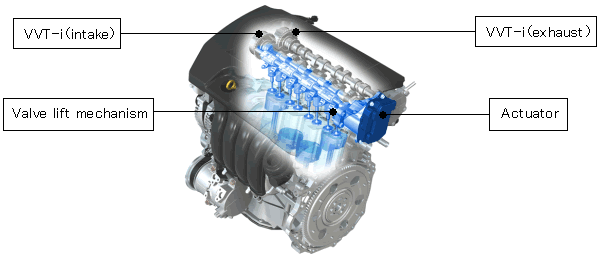
Tokyo ― TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION (TMC) announced today that it has developed Valvematic*, a variable valve lift mechanism created through combining VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent), which continuously controls intake valve opening/closing timing, with a new mechanism that continuously controls the intake valve lift volume.
While conventional engines control air intake using a throttle valve, Valvematic adjusts the volume of air taken in by continuously controlling the intake valve lift volume and timing of valve opening and closing. This ensures optimal performance based on the engine's operational condition, thus helping vehicles achieve both high fuel efficiency and dynamic performance.
In the case of a new 2.0-liter engine developed by Toyota, Valvematic―which further evolves the gasoline engine―improves fuel efficiency by 5% to 10% (depending on driving conditions), reduces CO2 emissions, boosts output by at least 10% and enhances acceleration responsiveness. TMC plans to introduce Valvematic shortly, starting with a new vehicle model featuring a 2.0-liter engine.
TMC positions global environmental preservation and initiatives toward energy diversification as a priority management issue in terms of its corporate social responsibility. As a part of its efforts to reduce CO2 emissions through high fuel efficiency and to achieve cleaner exhaust emissions, TMC plans to completely revamp its gasoline engine and transmission lineup by 2010.