Oct. 11, 2013
Toyota to Launch Advanced Driving Support System Using Automated
Driving Technologies in Mid-2010s
Safer Highway Driving; Reduced Environmental Effects and Driver Workload
Toyota City, Japan, October 11, 2013―Toyota Motor Corporation announces that it has developed a next-generation advanced driving support system, Automated Highway Driving Assist (AHDA), which uses automated driving technologies to support safer highway driving.
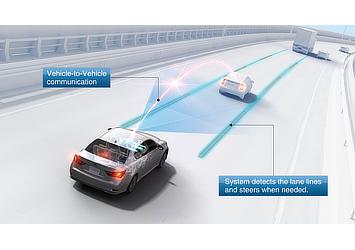
AHDA links two automated driving technologies to support safer driving and reduce driver workload: Cooperative-adaptive Cruise Control, which wirelessly communicates with preceding vehicles to maintain a safe distance; and Lane Trace Control, which aids steering to keep the vehicle on an optimal driving line within the lane.
Toyota recognizes the importance of the driver being in ultimate control of a vehicle and is therefore aiming to introduce AHDA and other advanced driving support systems where the driver maintains control and the fun-to-drive aspect of controlling a vehicle is not compromised. Toyota plans to market the newly developed AHDA in the mid-2010s and other driving support systems as soon as possible to provide safe and secure means of transportation.
Ahead of trials on the Shuto Expressway near the Tokyo metropolitan area starting October 15, Toyota will exhibit AHDA at the 20th Intelligent Transport Systems World Congress Tokyo 2013, an international conference for intelligent transport systems (ITS), to be held from October 14 to 18.
In addition, to enable prompt market introduction of next-generation driving support systems, Toyota will make use of the cutting-edge component technologies and know-how acquired through automated driving research conducted with the advanced active safety research vehicle unveiled at the 2013 International CES in Nevada, United States in January this year.
AHDA links two automated driving technologies to support safer driving and reduce driver workload: Cooperative-adaptive Cruise Control, which wirelessly communicates with preceding vehicles to maintain a safe distance; and Lane Trace Control, which aids steering to keep the vehicle on an optimal driving line within the lane.
Toyota recognizes the importance of the driver being in ultimate control of a vehicle and is therefore aiming to introduce AHDA and other advanced driving support systems where the driver maintains control and the fun-to-drive aspect of controlling a vehicle is not compromised. Toyota plans to market the newly developed AHDA in the mid-2010s and other driving support systems as soon as possible to provide safe and secure means of transportation.
Ahead of trials on the Shuto Expressway near the Tokyo metropolitan area starting October 15, Toyota will exhibit AHDA at the 20th Intelligent Transport Systems World Congress Tokyo 2013, an international conference for intelligent transport systems (ITS), to be held from October 14 to 18.
In addition, to enable prompt market introduction of next-generation driving support systems, Toyota will make use of the cutting-edge component technologies and know-how acquired through automated driving research conducted with the advanced active safety research vehicle unveiled at the 2013 International CES in Nevada, United States in January this year.

AHDA maintains inter-vehicle distance

Advanced Active Safety Research Vehicle
Automated Highway Driving Assist (AHDA)
Cooperative-adaptive Cruise Control
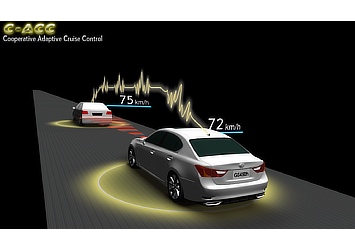
In contrast to standard radar cruise control (which uses millimeter-wave radar to detect other vehicles), Cooperative-adaptive Cruise Control uses 700-MHz band vehicle-to-vehicle ITS communications to transmit acceleration and deceleration data of preceding vehicles so that following vehicles can adjust their speeds accordingly to better maintain inter-vehicle distance. By reducing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, the system improves fuel efficiency and helps reduce traffic congestion.
Lane Trace Control
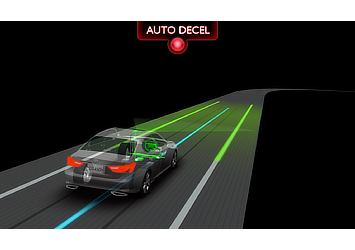
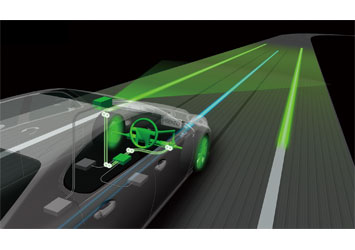
Lane Trace Control, which features completely new Toyota automated driving technologies, employs high-performance cameras, millimeter-wave radar and control software to enable an optimal and smooth driving line at all speeds. The system adjusts the vehicle's steering angle, driving torque and braking force when necessary to maintain the optimal line within the lane.
Cooperative-adaptive Cruise Control
In contrast to standard radar cruise control (which uses millimeter-wave radar to detect other vehicles), Cooperative-adaptive Cruise Control uses 700-MHz band vehicle-to-vehicle ITS communications to transmit acceleration and deceleration data of preceding vehicles so that following vehicles can adjust their speeds accordingly to better maintain inter-vehicle distance. By reducing unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, the system improves fuel efficiency and helps reduce traffic congestion.
Lane Trace Control
Lane Trace Control, which features completely new Toyota automated driving technologies, employs high-performance cameras, millimeter-wave radar and control software to enable an optimal and smooth driving line at all speeds. The system adjusts the vehicle's steering angle, driving torque and braking force when necessary to maintain the optimal line within the lane.
Automated Driving Technologies Research
At the 2013 International CES, Toyota displayed the advanced active safety research vehicle, a test vehicle for automated driving technologies that Toyota is researching under its Integrated Safety Management Concept1. The test vehicle, based on the Lexus "LS", is being used in research at the Toyota Research Institute of North America in Saline, Michigan, and is capable of autonomous driving. It is fitted with forward-looking cameras to detect traffic signals, as well as front-mounted sensors to detect vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles to determine traffic conditions, such as intersections and merging traffic lanes, in the vehicle's vicinity. Such research on various elemental technologies is aimed to help drivers choose the safest routes possible.
Toyota has been researching automated driving technologies since the second half of the 1990s, and has been conducting public road tests in the U.S. for a number of years. Within Japan, Toyota has been testing its next-generation Intelligent Driver-support System on public roads2 for approximately two years.
Based on the insights gained from automated driving research, Toyota aims to provide advanced driving support systems optimized to help enable safer driving and contribute to realizing the ultimate goal of any society that values mobility: the elimination of traffic fatalities and injuries.
In anticipation of the super-aging populations of the future, these advances will also be used to develop technologies that support senior drivers with recognition, decision-making and vehicle operation, with the aim of achieving a mobility society where they can lead fuller lives. Furthermore, Toyota is working to provide more stable driving environments that contribute to the alleviation of traffic congestion, thereby reducing economic loss and CO2 emissions.
At the 2013 International CES, Toyota displayed the advanced active safety research vehicle, a test vehicle for automated driving technologies that Toyota is researching under its Integrated Safety Management Concept1. The test vehicle, based on the Lexus "LS", is being used in research at the Toyota Research Institute of North America in Saline, Michigan, and is capable of autonomous driving. It is fitted with forward-looking cameras to detect traffic signals, as well as front-mounted sensors to detect vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles to determine traffic conditions, such as intersections and merging traffic lanes, in the vehicle's vicinity. Such research on various elemental technologies is aimed to help drivers choose the safest routes possible.
Toyota has been researching automated driving technologies since the second half of the 1990s, and has been conducting public road tests in the U.S. for a number of years. Within Japan, Toyota has been testing its next-generation Intelligent Driver-support System on public roads2 for approximately two years.
Based on the insights gained from automated driving research, Toyota aims to provide advanced driving support systems optimized to help enable safer driving and contribute to realizing the ultimate goal of any society that values mobility: the elimination of traffic fatalities and injuries.
In anticipation of the super-aging populations of the future, these advances will also be used to develop technologies that support senior drivers with recognition, decision-making and vehicle operation, with the aim of achieving a mobility society where they can lead fuller lives. Furthermore, Toyota is working to provide more stable driving environments that contribute to the alleviation of traffic congestion, thereby reducing economic loss and CO2 emissions.
1The concept does not refer to the individual safety systems on the car, but the integration of those systems to offer the optimum driving support at "all driving stages" from parking, to normal operation and the moments before and after a collision, and even avoidance at the moment of an accident.
2During testing, the driver maintains awareness of safety conditions and takes control of the vehicle whenever necessary.
2During testing, the driver maintains awareness of safety conditions and takes control of the vehicle whenever necessary.