Feb. 12, 1998
Toyota to Strengthen Its Automobile Recycling Efforts
To Build Plant for Full-Scale Practical Use of Shredder Dust
Tokyo―TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION (TMC) announced today that it will further enhance its efforts in vehicle recycling. TMC always has considered environmental protection as one of the most important aspects of its operations. It has based such activities on the "Toyota Earth Charter" (established January 1992) and the "Toyota Environmental Action Plan" (established February 1993; amended April 1996), which last year were intensified even further under the "Toyota Eco Project." Today's announced plan reinforces numerous activities already underway.
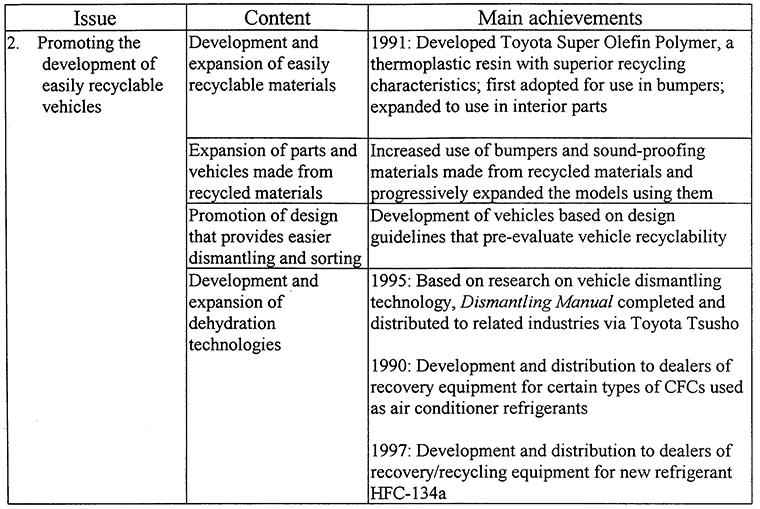
- Outline of Reinforcement PlanToyota's recycling activities are steadily bearing fruit. In 1996, it achieved the goal of building a new car that is 85% recyclable by weight. Nonetheless, TMC still aims to raise the recyclable rate to 90% by the year 2000, which is two years earlier than the deadline set in the Ministry of International Trade and Industry's (MITI) Recycling Initiative for End of Life Motor Vehicles. At the same time, Toyota is also promoting a comprehensive approach that covers the overall life cycle of automobiles, from development, through production and use, to scrapping.
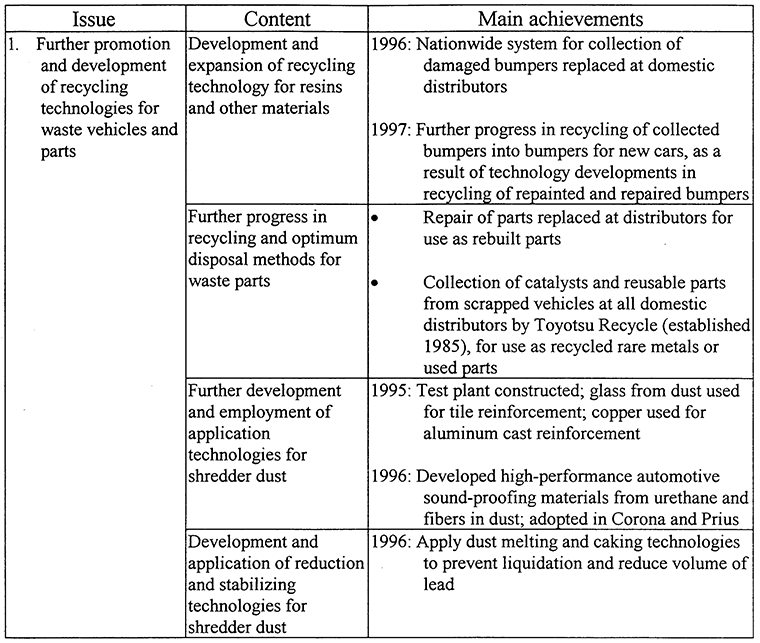
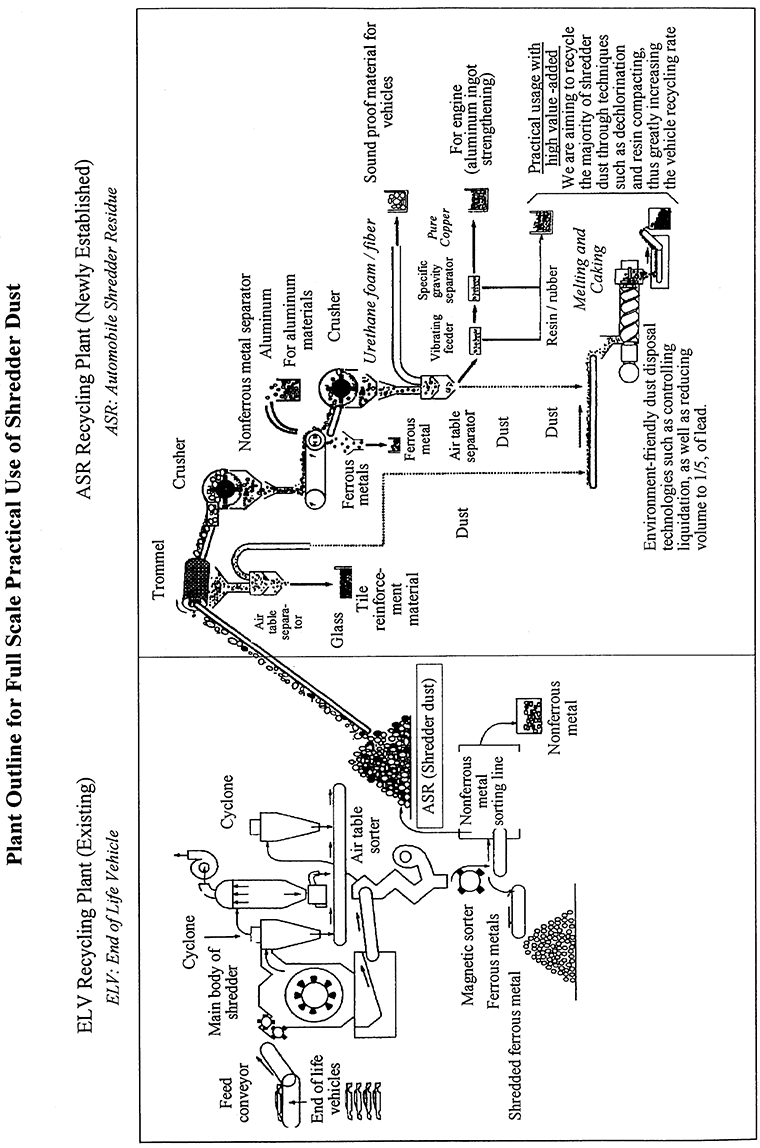
The plan announced today aims to improve Toyota's overall recycling activities by strengthening the following specific points.- Building a plant for full-scale practical use of shredder dustToyota Metal Co. was established in 1970 and grew to become one of Japan's largest capacity vehicle shredder plants, accumulating a wealth of know-how along the way.The technology used to transform shredder dust into a high performance sound proofing material, which was born of Toyota Metal's experience, was subsequently confirmed at a test plant. Based on those positive results, the world's first full-scale plant for recycling shredder dust will be established at Toyota Metal and will begin operations this August.As a result, the volume of melted and caked shredder dust generated by Toyota Metal that must be disposed of by burial will be reduced by the year 2000 to one-fifth or less of its present volume. Toyota thus expects to achieve a remarkable 15 years in advance the targets for 2015 set in MITI's Recycling Initiative for End of Life Motor Vehicles.
- Recycling of nickel-metal hydride batteriesIn cooperation with Panasonic EV Energy Co., Ltd., a system will be established for recovery of all Ni-MH (nickel-metal hydride) battery units used in the Prius hybrid passenger car that Toyota began mass producing at the end of 1997.In parallel, Toyota is also moving forward with early development of what would be a world first technology for the use of recycled batteries in new batteries.
- OtherToyota is also working to address other important issues, such as, by the year 2000, equipping all models with air bag connectors standardized by the Japan Automobile Manufacturer's Association, which will make it easier for vehicle air bags to inflate. TMC also plans to reduce the use of lead (excluding lead in batteries) in new cars to at least one-half the current amount by 2000, and one-third by 2005.
- Building a plant for full-scale practical use of shredder dust
- Intensified ActivitiesBased on the revised Toyota EnvironmentalAction Plan, in addition to the goal of increasing vehicle recyclability to 90% by the year 2000, Toyota continues to strengthen its efforts in the following areas.