Apr. 07, 1998
Toyota Takes ISO 14001 Certification for
Product Environment Management System
First Automaker in Japan for Such Certification
Tokyo―TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION obtained ISO 14001 certification for its Product Environment Management System in March of this year. Toyota became the first domestic automaker to obtain such certification in the product design and development field.
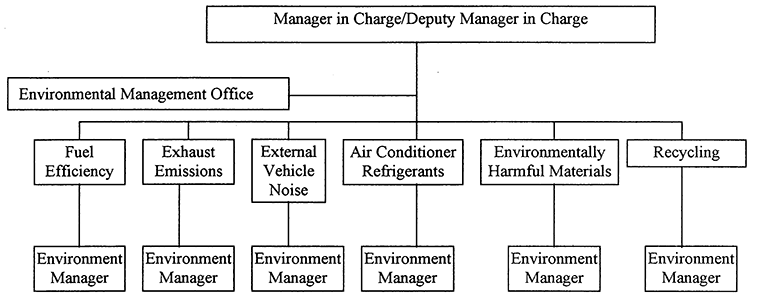
The new system promotes the design and development of vehicles that reduce the burden on the environment in the use and disposal stages. These two stages are believed to have the largest environmental impact during a vehicle's life cycle. Toyota's system is based on self-imposed, quantitative goals in each of six areas: (1) fuel efficiency, (2) exhaust emissions, (3) external noise, (4) air conditioner refrigerants, (5) environmentally harmful substances, and (6) recycling.
Toyota has been promoting product development based on this system, starting with the new Harrier announced in December 1997. Toyota will apply the system to the development of a series of new models it plans to launch.
Toyota also has taken the initiative in obtaining certifications for its production plants. Among the domestic plants with ISO 14001 certification are Takaoka (Mar. '96), Tsutsumi (Dec. '96), Motomachi (Aug. '97), and Tahara (Dec. '97). Overseas plants include TMUK in the United Kingdom (Sept. '96), TMT Gateway in Thailand (Dec. '97), TMCA Altona in Australia (Jan. '98), and CAPTIN in Canada (Dec. '97). Toyota plans to obtain certification at all domestic operations and major overseas operations by the end of 1999.
ISO 14001 is an international environment management standard aimed at reducing the environmental burden of industrial activities. It was formulated in 1996, and since then companies worldwide have been introducing environmental management systems based on it and acquiring certification from third party inspection registration authorities. Toyota's certification came from the Japan Automobile Research Institute, Inc., which specializes in inspections and registrations in the transportation equipment field.
Reference MaterialProduct Environment Management System Details
- Management Policy and Targets
Chart 1. Product Environment Policy
- We will vigorously engage in product development with a consideration for the global environment, regional society, and the sources that generate waste material.
- We will move to prevent pollution by closely adhering to environmental legislation and by setting our own environmental standards.
- We will carry out environmental audits, take steps to manage ourselves, and continuously strive to improve our environmental performance.
- Each employee will be aware of the importance of environmental measures that consider the overall product life cycle, thereby helping lessen detriment to the environment.
Chart 2. Target Areas and Objectives for "Product Environment Management"

- *Note
- Current objectives are as shown in this chart, but ongoing reviews will be made to upgrade the levels.
- Management Organization