Sep. 19, 2023
Monozukuri technology to support the future
Table of contents
Changing the plant status quo and the future of manufacturing
- Toyota is also taking on the challenge of further advancing manufacturing by integrating the skills/technologies that support the workplace with digital and innovative technologies.
- One of the front-line capabilities that Toyota has continued to protect to date is the ability to shorten lead times. By refining this capability, we can respond quickly to changes, and at the same time, we are working on next-generation manufacturing and solving social issues without fear of failure.
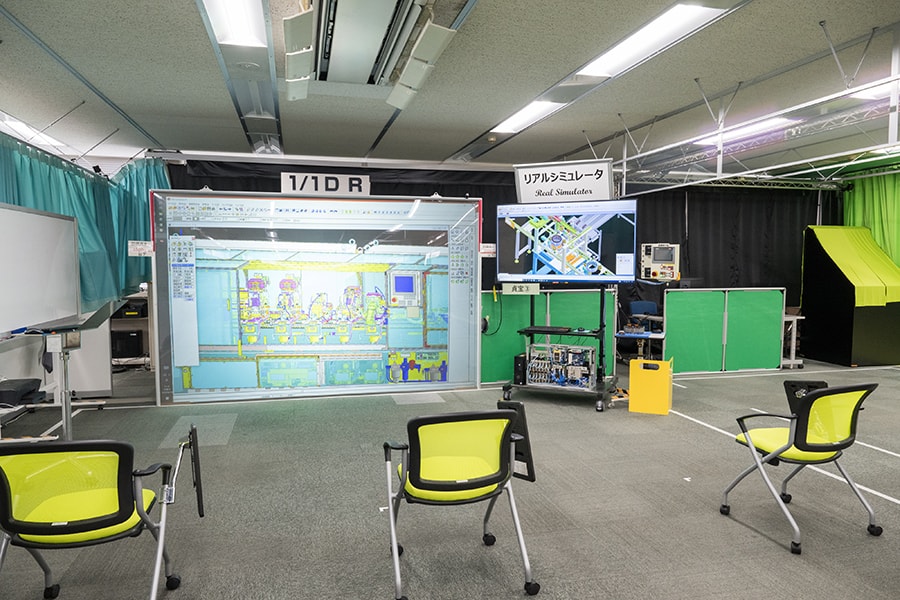
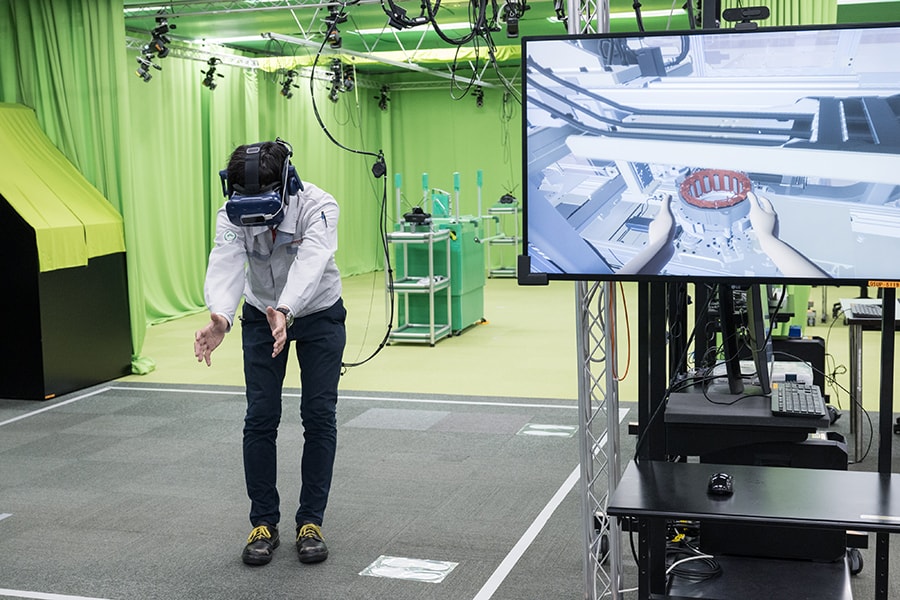
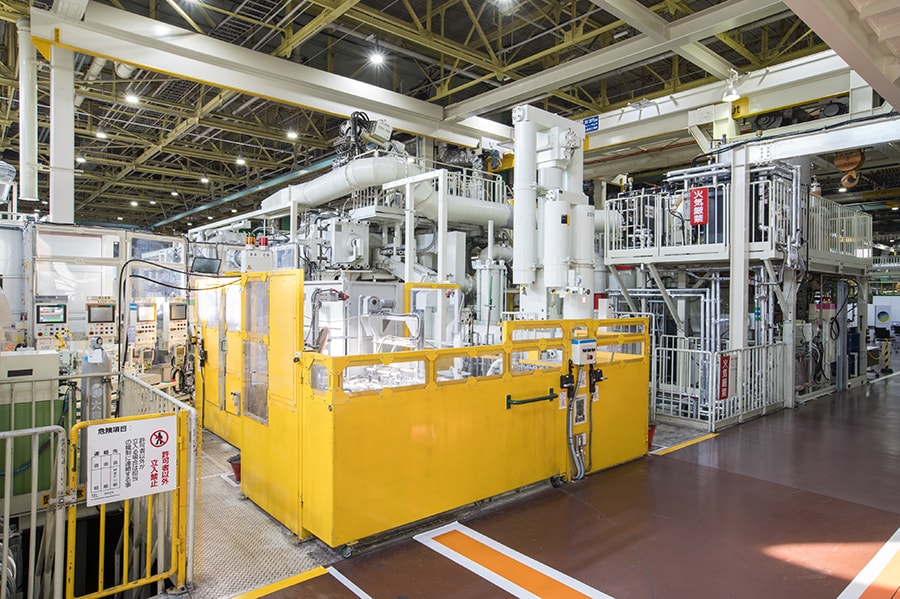
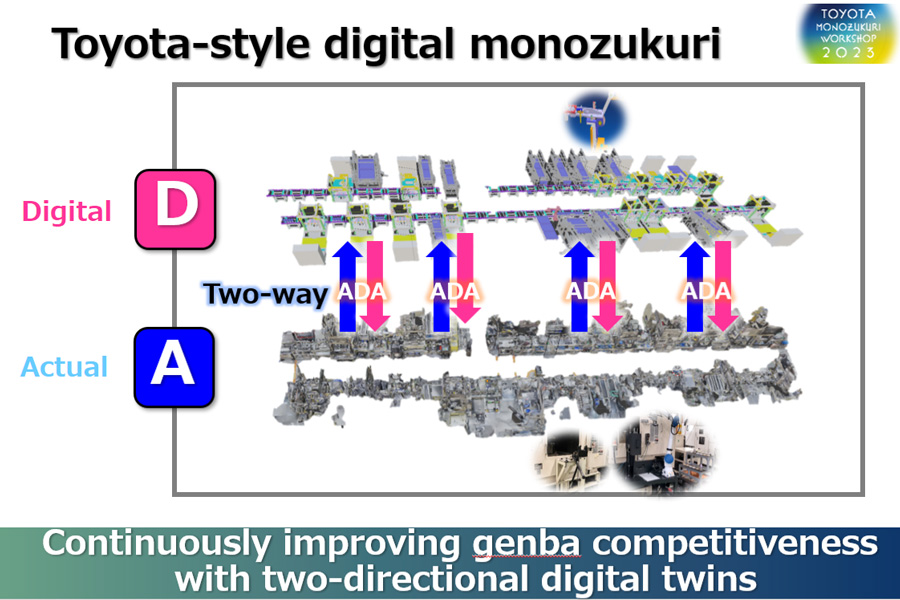
Equipment manufacturing using a digital twin (Teiho Plant)
- To deliver products that customers want at the time they want, it is necessary to start up production facilities capable of manufacturing products in a timely manner. However, in the process of launching new production facilities, defects and difficulties may be found that were not anticipated on the drawings, resulting in wasteful redoing and long lead times.
- To address this issue, a digital environment was utilized to create a 3D model, or digital twin, first, allowing equipment designers, manufacturers, and customers, to identify potential defects in advance. As a result, the knowledge and experience of Toyota's front-line workers are incorporated into the 3D model from the design stage, and the equipment can be introduced as a highly refined system to the shop floor without having to be redesigned, cutting the lead time from design to the start of production in half.
- Many people, both inside and outside the company, are involved in building the facilities that produce cars. The more widespread the use of digital twins in equipment manufacturing, the greater the potential to further reduce lead time and promote productivity improvements.
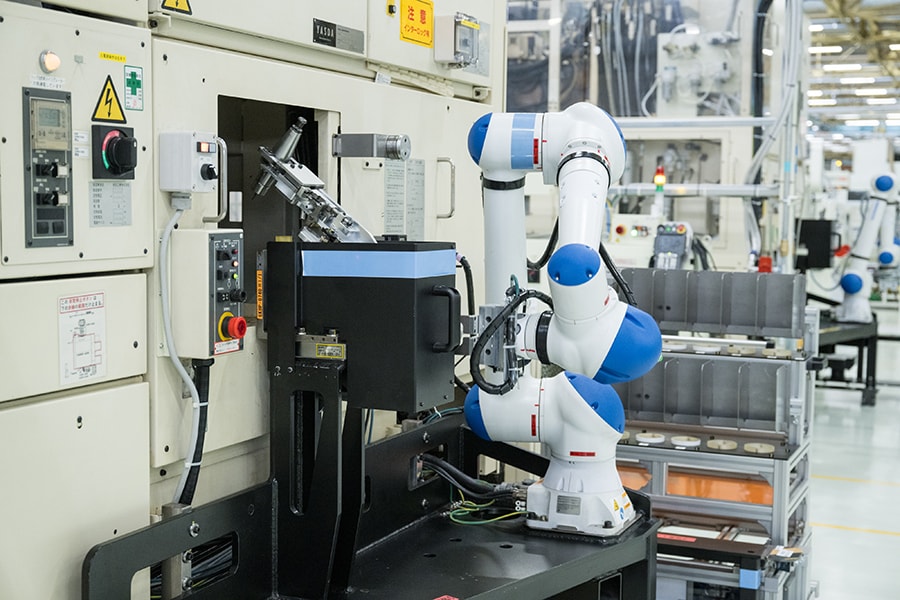
Productivity Improvement of existing facilities with digital twin (Teiho Plant)
- By creating 3D models of existing facilities and adding improvements inspired by front line skills, we are working to improve productivity with reduced lead times. We are taking on the challenge of creating Toyota-style Monozukuri through an interactive digital twin that reflects digital improvements in the real workplace. This approach has also led to the additional automation of work.
- At the Teiho Plant mold and equipment parts processing facilities, material loading and other operations that had previously relied on human labor were improved and automated using the 3D model, which was then able to be reflected at the real facility. Productivity tripled, and lead times were reduced to one-third of the previous times.
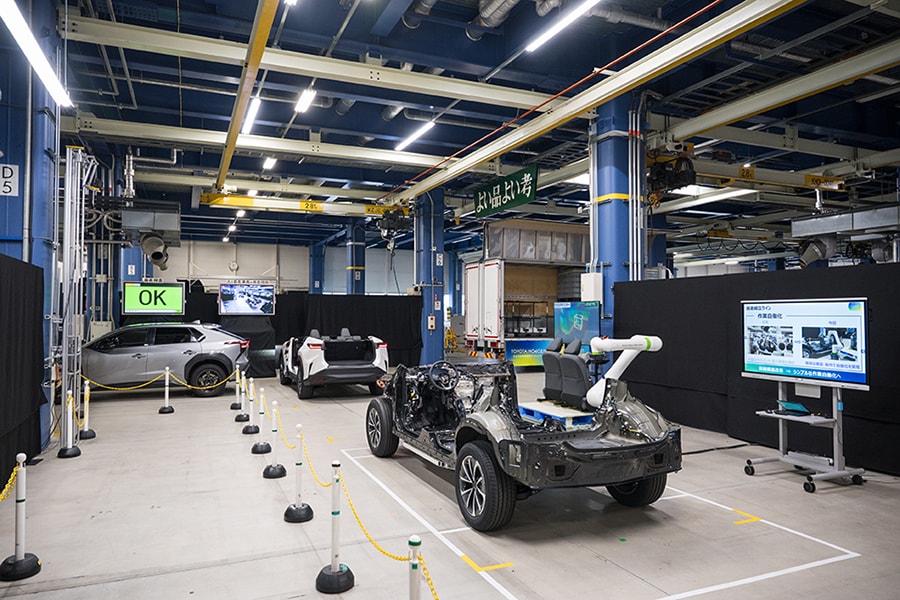
Next-generation BEV practical demonstration line (Motomachi Plant)
- At the current workshop, Toyota revealed part of the preparation status of the next-generation BEV production line announced at the Toyota Technical Workshop held in June 2023.
- On the next generation BEV production line, we aim to change the status quo for manufacturing for the new modular structure and self-propelled production to account for 1/2 of the process and plan investment.
- Improving work efficiency, increasing productivity, and shortening lead times are what TPS does best. We are taking on the challenge of creating new products by combining the experience and skills we have cultivated in car manufacturing to date with new technologies.
- The three-part modular structure (front, center, and rear) allows work to be performed in an open environment, which improves work efficiency and productivity and reduces processes compared to work conventionally performed with people inside the frame.
- Toyota insources all kinds of technologies for its equipment and vehicles. The self-propelled conveyance with finished vehicles that was put to practical use at the Motomachi Plant was achieved by combining control technology cultivated through the development of autonomous driving with sensor technology for recognizing people, vehicles, and the environment installed at the plant. This technology has now been applied to enable stable traveling at extremely low speeds, at the level of a conveyor. Applying this technology to next-generation BEV lines greatly improve line layout flexibility.
- This can significantly reduce production preparation lead time and plant investment. A simple conveyor-less process has already been implemented on some welding lines at the Motomachi Plant. We will provide feedback on issues and further develop a self-propelled assembly line for the next-generation BEV line.
Giga casting (Myochi Plant)
- The workshop revealed prototype equipment for the Giga casting technology at the Myochi Plant that was announced at the Toyota Technical Workshop held in June 2023.
- Giga casting requires periodic replacement of casting molds, which usually takes about 24 hours. Toyota has a wealth of knowledge about molds used for low-pressure molding and die-casting, with casting technologies cultivated in engine manufacturing and other fields from the company's founding to the present. By utilizing this knowledge, an ingeniously designed mold has been developed that enables quick mold replacements. This reduces the lead time required for mold change to approximately 20 minutes, reducing wasted operation downtime.
- Furthermore, the use of proprietary analysis technology improves the quality of castings, thereby reducing the number of defective products. These TPS-based waste reductions ensure high productivity.
All-solid-state battery development line (Teiho Plant)
- All-solid-state batteries for BEVs, which was announced at the Toyota Technical Workshop held in June 2023, are undergoing product development, and the method for mass-production is being developed with the aim of commercialization in 2027-28. At the current workshop, Toyota is showing the process development site and a part of the planned mass production methods.
- Unlike liquid batteries, all-solid-state batteries have ions moving through a solid, so ideally, the anode, cathode, and solid electrolytic layers should be tightly adhered to each other without gaps. Toyota has achieved the difficult process of stacking batte.ries at high speed and high precision without damage to the battery materials in anticipation of mass production, using an innovative mechanism and synchronous control technology.
Development line for the popularization version of next-generation batteries (bipolar lithium-ion batteries) (Teiho Plant)
- The bipolar lithium-ion battery, the popularization version of the next-generation battery announced at the Toyota Technical Workshop in June 2023, is currently undergoing product development and the development method for mass production with the aim of commercialization in 2026-27. Today, Toyota revealed a coating process as part of the method development site for mass production.
- In the coating process, to maximize the performance of inexpensive lithium ferro phosphate (LFP), the paste must be applied to the metal foil evenly and in large quantities at a speed that allows for mass production. Toyota will be able to use its 26 years of battery production knowledge gained from HEVs and the equipment for applying high-speed coating technology developed for FC (fuel cells) to achieve this.
Carbon-neutral manufacturing (Motomachi Plant)
- Toyota will accelerate three initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality in manufacturing: daily improvements, innovation in Monozukuri, and the use of renewable energy and hydrogen.
- As part of our daily improvement activities, we utilize powerless equipment using "karakuri" (a mechanical gadget that helps improve productivity and reduce costs), and we have previously introduced airless painting technology to make the coating process more compact as a manufacturing innovation. In addition, we are promoting the use of renewable energy and hydrogen in cooperation with our partners in various countries, in accordance with regional characteristics.
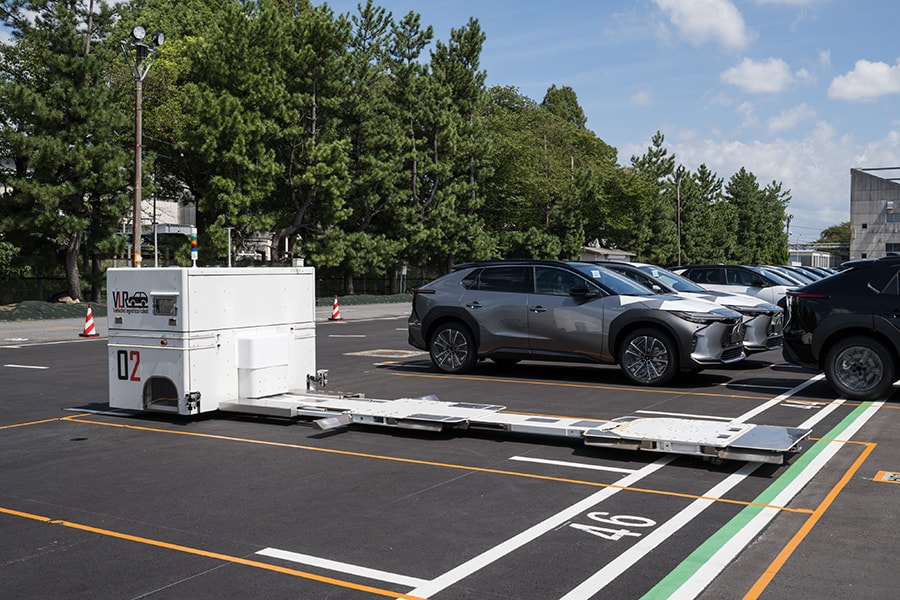
Addressing logistics issues with vehicle handling robots (Motomachi Plant)
- The logistics industry, including finished vehicle logistics, is facing a chronic shortage of labor, stemming from a reduction in transportation capacity due to stricter regulations on driver working hours, aging drivers and transport workers, and a high turnover rate. These are issues not unique to Toyota, but have been identified as issues for the industry as a whole, and there is an urgent need to reduce the workload of drivers and transport workers and to create an environment in which they can work with peace of mind.
- Toyota has installed roofs at loading/unloading areas at plants and ports across Japan to improve the working environment for drivers so that they can work safely even in bad weather.
- We are also working to improve the vehicle pickup process by drivers and haulers at finished vehicle yards. Vehicle transportation at the finished vehicle yard is currently done manually, and there is a chronic shortage of staff. Another issue is the physical burden of the work, which involves walking long distances outdoors.
- The Motomachi Plant introduced a Vehicle Logistics Robot (VLR) to reduce manpower and workload. It has the versatility to raise, lower, extend, and retract the cargo bed depending on the vehicle height/wheelbase to accommodate vehicles of different sizes. In addition to high-precision autonomous movement, a control system centrally manages the movements of multiple robots to monitor safety and enable transport along optimal routes. Also, unlike human transport, there is no need to open and close doors, enabling efficient arrangement of vehicles without gaps as a more efficient use of the yards.
"Achieving zero, and adding new value beyond it"
As part of efforts to pass our beautiful "Home Planet" to the next generation, Toyota has identified and is helping to solve issues faced by individuals and overall society, which Toyota calls "Achieving Zero," hoping to help reduce the negative impacts caused by these issues to people and the environment to zero. Additionally, Toyota is also looking "Beyond Zero" to create and provide greater value by continuing to diligently seek ways to improve lives and society for the future.
- About Beyond Zero
- https://global.toyota/en/mobility/beyond-zero/
Toyota Motor Corporation works to develop and manufacture innovative, safe and high-quality products and services that create happiness by providing mobility for all. We believe that true achievement comes from supporting our customers, partners, employees, and the communities in which we operate. Since our founding over 80 years ago in 1937, we have applied our Guiding Principles in pursuit of a safer, greener and more inclusive society. Today, as we transform into a mobility company developing connected, automated, shared and electrified technologies, we also remain true to our Guiding Principles and many of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals to help realize an ever-better world, where everyone is free to move.
- SDGs Initiatives
- https://global.toyota/en/sustainability/sdgs/